Mayfair: A Modular Case Study
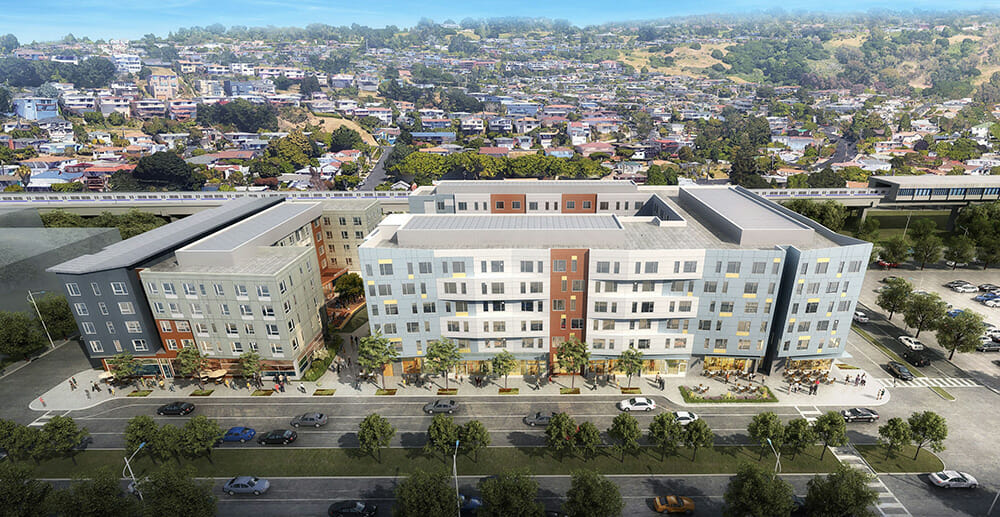

Previously used as a surface parking lot for commuters accessing public transit, the Mayfair development on a city-owned block in El Cerrito, Calif. brings 223 new housing units to a long-neglected stretch near the El Cerrito del Norte Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) Station.
The affordable and market-rate units will be in their own U-shaped buildings that surround a pair of open courtyards. The central open space between buildings will be open to the public during daylight hours to encourage activity in the transit-oriented development. 67 of the units will be classified as affordable housing, ranging in affordability from 30% – 60% of area median income.
The program mix between the two buildings consist of 10,500 sf of ground floor retail, parking, bicycle parking, property management, community rooms, dog wash and tenant service offices as amenities available for tenants. Program open space will include play areas, vegetable gardens, BBQ area and an outdoor kitchen.
Named for the grocery chain that once occupied the block, The Mayfair project received its first stacked module unit October 2020 and reached its full building height of six stories after ten days of assembly.
The modules for the 156-market rate units of the project started production in June 2019. The modules were fabricated by Factory_OS, only 19 miles away from the site in Vallejo, Calif.
Design Intent
This project sits on a dynamic site in terms of passers-by. It is located on a major thoroughfare (San Pablo Ave.), next door to the El Cerrito del Norte BART stop and regional transit hub. The building façade was envisioned to push the boundaries of modular design while creating a dynamic expression that could hold up to the power of the site. Responding to the movement of the BART trains, the design has horizontal undulating angles that stagger between floors, not common in modular construction.
Normally, a site bounded by heavy traffic and a major public transit line would seek to turn itself inward to protect against these challenges to living; however, the design instead opens toward the BART parking lot with a two-story portal that offers glimpses into the inner courtyard and puts the building’s common space on display for the neighborhood to see.
The plan was arranged with building circulation in a single loaded corridor on the exterior, where the façade faces the BART track. This serves as a sound buffer to the interior units and creates a mostly solid area of the façade that will have a large-scale public artwork facing BART.
Rounding out the aesthetics, the design team is working with a local artist on an installation incorporating areas of mirrored building skin that will blur and change daily for commuters on BART. The idea is that as the time of day and colors of sky change, the rider approach and experience of passing by the building will be unique.
Related Reading:
Modular Design Through the Construction Perspective
Unlike traditional, site-built projects, modular projects require a significant amount of up-front coordination, not just on design, but with project scheduling and factory bidding. This article explores how development teams will benefit from a deeper understanding of some of the contractor’s considerations unique to the modular approach.

Modular Highlights
Initially, the Mayfair project was considered unbuildable as a modular project, given the complexity of exterior façade design. The architect and engineering team collaborated to figure out the best way to build the exterior envelope, which included the following challenges:
- Articulation – Façade articulation was very important to this project. To break up the façade plane, the design was broken horizontally – an aesthetic element that contextually related to the nearby BART tracks and station. In achieving this, the placement of shear walls needed to be strategically coordinated with the structural engineer. With no repeating, stacking façade elements, the modular manufacturer had to be onboard to fabricate the building. The two-story, site-built portal design required coordination with the structural engineers and the factory to get the final installation to work.
- Portal Design – The site-built portal is made up of both steel and wood framing construction. The design element is intended to activate the southern portion of building and support the modular units that sit above and adjacent to the opening. The coordination of steel placement was achieved with the help of a third-party clash detection agency, which was critical to overlay factory as-built conditions with site construction.
- Single Loaded Corridor – The eastern portion of the building consists of a single loaded corridor. Though saw box units are generally not efficient in modular design, here, they allow the eastern corridor to face the street while the units face the courtyard – a move necessary to achieve the desired density of units. The single loaded corridor also allows for an acoustic buffer and provides space for innovative art panel installation at the eastern exterior wall.
- Combination of Factory + Site Built for Common Rooms – Requested by planning to activate the façade, the common rooms were site built from structural steel, allowing for a greater span for programming including a lounge adjacent to the two-story portal and across from a fitness space.
Project Specifications
- Type 3A Construction
- Estimated completion: June 2021
- Team:
- Lowney Architects
- DCI Engineers
- FARD Engineers
- Cannon Cononstructors
- Factory_OS
- Holliday Development
More from Modular Advantage
How Stack Modular Is Using AI to De-Risk Mid- to High-Rise Modular Construction
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept in modular construction—it is already reshaping how complex buildings are evaluated, designed, and delivered.
Gearing Up for the 2026 World of Modular
The Modular Building Institute (MBI) is bringing its global World of Modular (WOM) conference and tradeshow back to Las Vegas in April, and with it comes some of the industry’s best opportunities for networking, business development, and education.
New High-Rise Modular Apartment in Abu Dhabi Points Toward the Future of Multifamily Construction
Eagle Hills International Properties chose the BROAD Holon Building for a 16-story market rate apartment building in Zayed City, a central business district of Abu Dhabi. The project highlights the potential of the Holon system of volumetric modular construction to accelerate housing delivery.
MBI Announces First Ever Industry Apprenticeship Program in Collaboration with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center
MBI recently agreed to partner with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center (MAMC) to provide bona fide USDOL-approved apprenticeship programs for the industry.
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.