What’s Next: UNB OCRC Student Competition Previews the Future of Offsite Building
For the second year in a row, the University of New Brunswick’s Off-Site Construction Research Centre (OCRC), a research group dedicated to optimizing alternate solutions to on-site construction, presented its Off-site Construction Student Design Competition in partnership with the OSCO Construction Group. This competition—sponsored again by the Modular Building Institute—showcased student design innovation in modular, prefabricated, panelized, and other types of off-site construction and featured entries from dozens of interdisciplinary collegiate teams.
The objective of the competition was simple: to introduce students to offsite construction and to encourage interdisciplinary collaboration. It was also an opportunity to showcase how offsite construction’s many benefits, including reduced construction timelines, improved safety, and improved construction quality, can benefit the construction industry.
The Challenge
This year’s teams were challenged to design and present plans for a residence building for the University of New Brunswick (Fredericton) campus. The building needed to be at least 50% prefabricated, and the proposal needed to demonstrate how an offsite solution can address the project needs. Students were encouraged to consider pre-cast elements, sustainable, green technologies in their solutions.
Project Requirements:
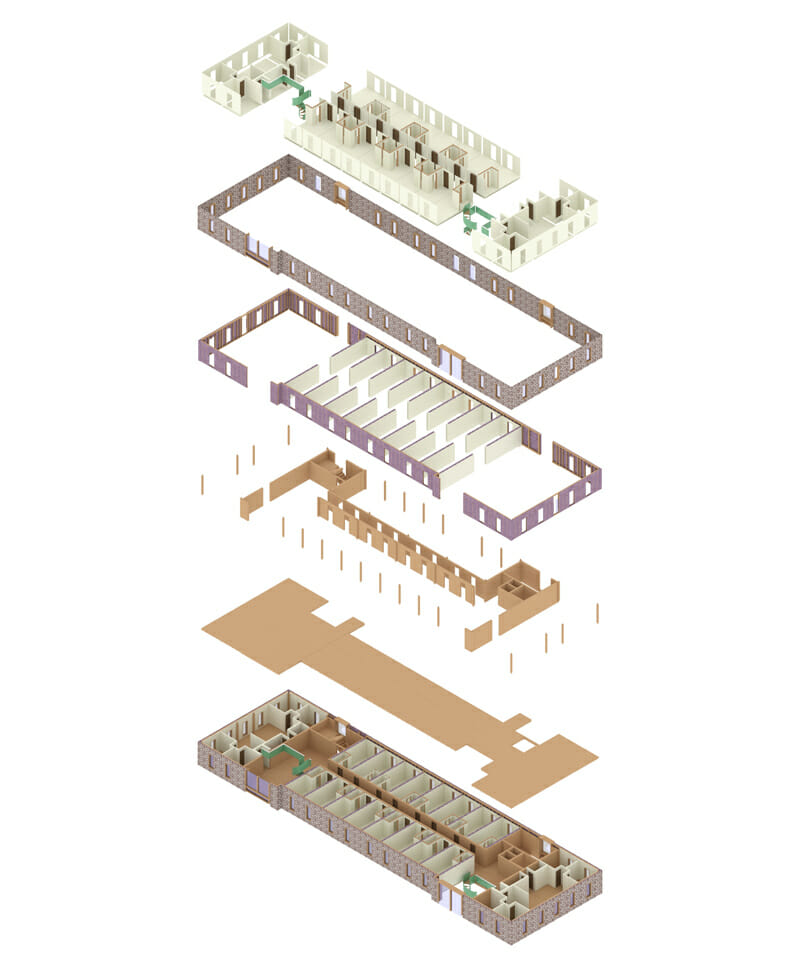
- Design a new residential/commercial structure to replace an existing structure on campus, including 3D renderings, technical drawings, assembly diagrams, and more
- New structure should include a daycare facility and commercial space on the first floor
- Upper levels of the new structure to be living spaces
- Targeted to be a LEED Gold and net zero building
- Other aspects to consider:
o Demolition methods
o Parking lot
o Construction methods and sequencing, considering the nearby school zone
o Local bylaws and zoning
o Inclusiveness and accessibility in the design
o Incorporation of Indigenous art
Judging Criteria
The entries were judged using three criteria:
- 25% graphic presentation/design
- 50% creative demonstration of the potential of offsite construction
- 25% project feasibility/buildability
“OCRC is always innovating new ways to move away from the traditional “stick-built” construction into prefabricated and off-site construction. We work with many student researchers for our projects and know the kind of value they bring. We had ideated the Off-site Construction Student Design Competition to present students with a fun learning-based opportunity to help put their innovations in front of a larger audience, get expert feedback, and showcase their abilities simultaneously. The second year of doing this competition brought in many great ideas that showcased prefabricated and off-site focused mixed commercial and residential buildings that are sustainable and meet the need of the hour. We would like to thank MBI for their continued support of the competition.”
Brandon Searle, Director, Innovation and Operations, OCRC, University of New Brunswick
The Winners
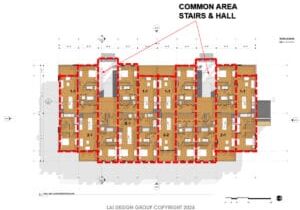
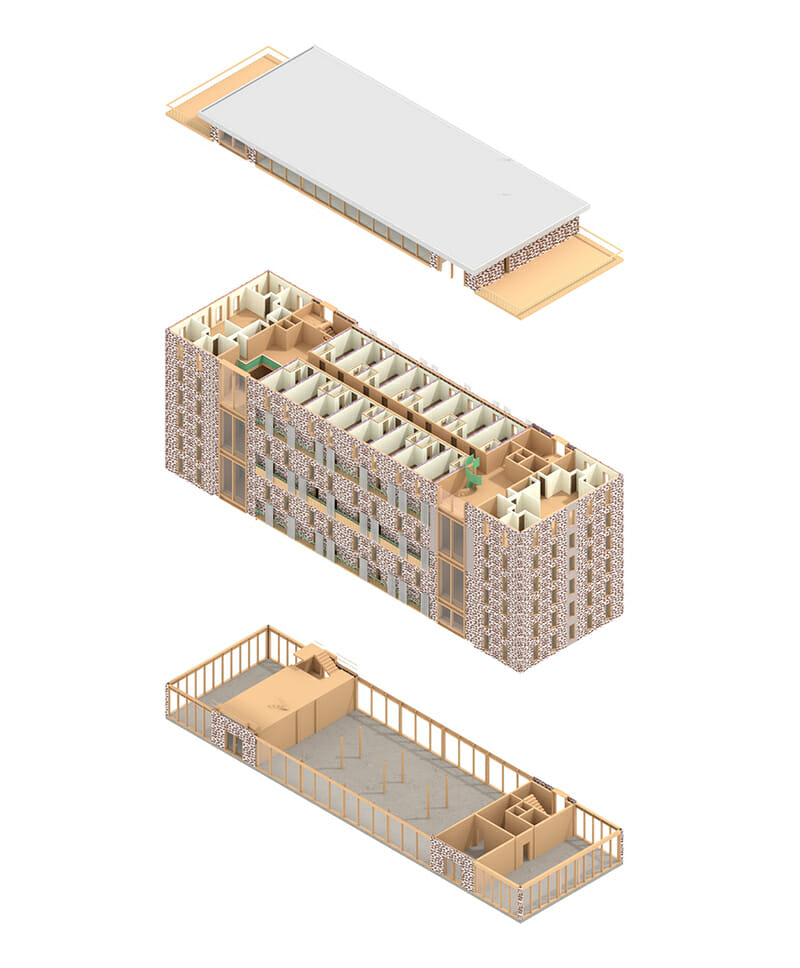
First Place: The Montgomery Complex
Team members: Anneliese Sirju, Luisa Prestes, Luz Almazan Martinez, Leslie Anne Bugayong, Julianne Brewer, Jiyoung Park, Hyoung Sik Yoon, and Ming Kai Tang (Southern Alberta Institute of Technology)

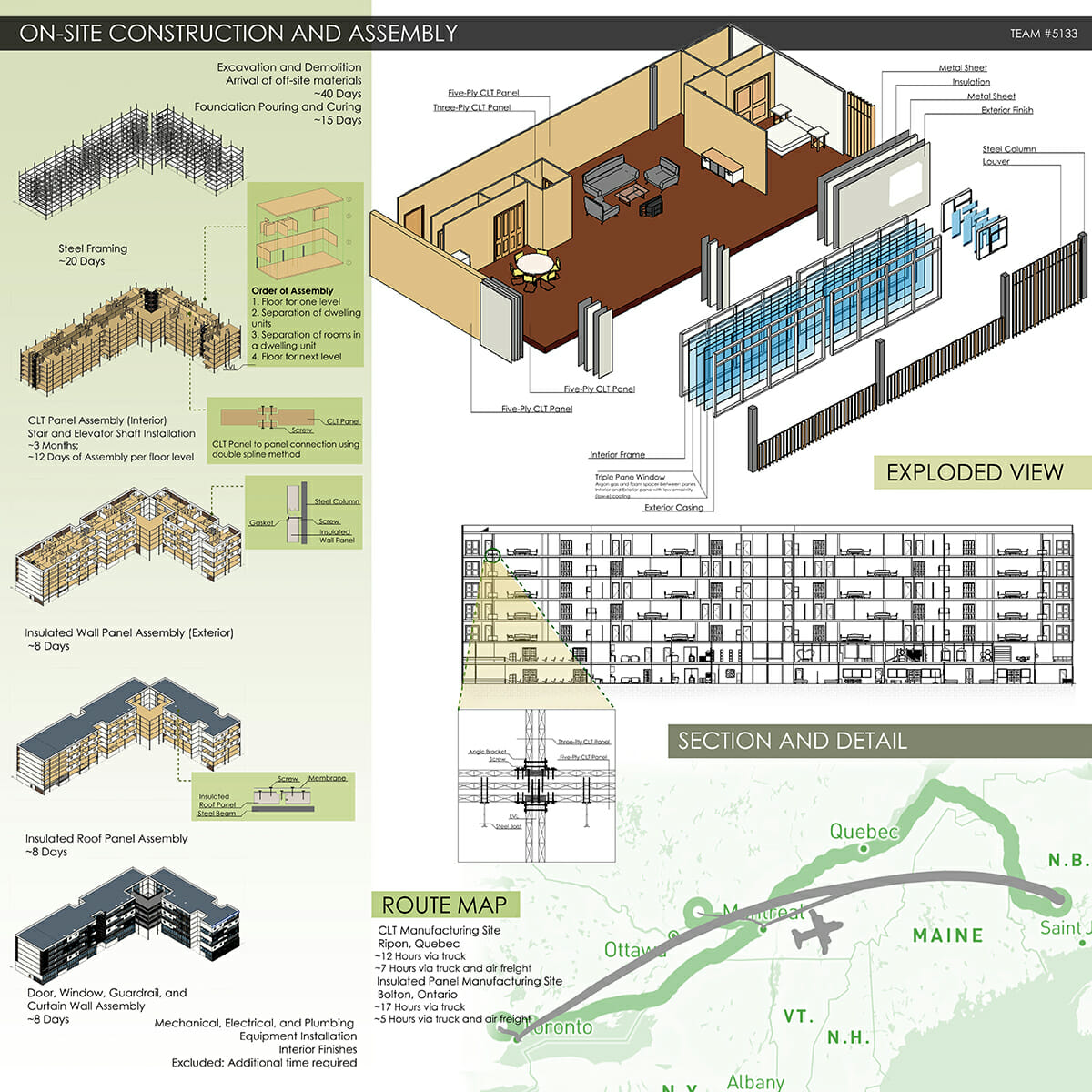
“More than student residence, The Montgomery Complex includes spaces that enhance the life of the students and their families. It strives to connect with native roots using Mi’kmaq patterns in its façade but also provides walls for local talent’s art. With a combination of steel and mass-timber, this building aims to create a positive impact in the area, offering a new type of conscious architecture.”
“We started developing the geometry of the design by using the existing buildings footprint as reference,” says team leader Luz Almazon. “Our first ideas leaned towards an L-shaped building which later evolved into two towers connected by terraces. This final itineration allowed us to stay within a scale that was not too overwhelming in terms of design.”
Teammate Leslie Bugayong added, “The majority of the walls would be built offsite. The interior CLT panels could be manufactured nearby while exterior walls would be insulated panels.”
“Construction would be efficient, more sustainable than using traditional methods, and could set the standard for a new type of architecture in the area,” concluded Almazon.
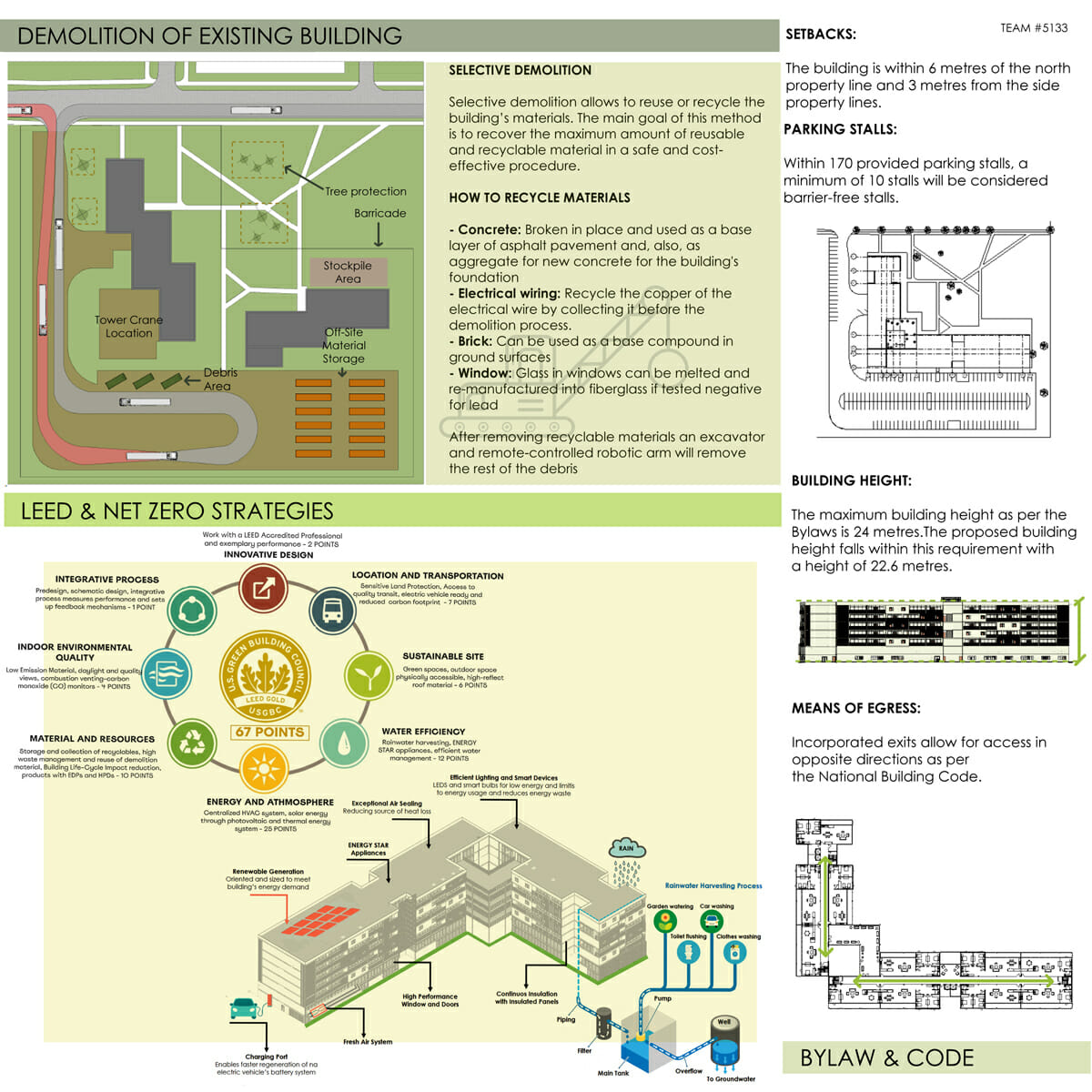
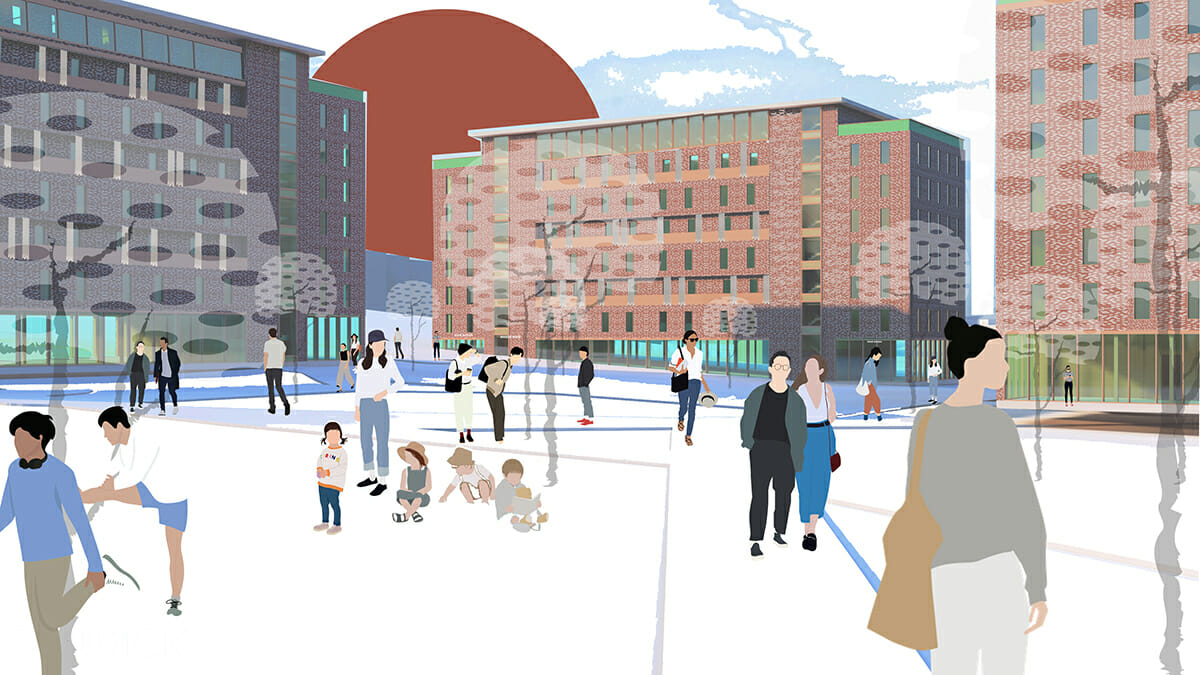
Second Place: The Magee-Mcloud Housing
Team members: Simon-Olivier Fortin, Sarah Samsoudin, and Charles-Emmanuel Lambert (Université du Québec à Montréal)

“We started working on the plans with a grid pretty early on in order to coordinate the structure and the layouts efficiently,” said team member Sarah Samsoudin. “We went through a lot of iterations while trying to figure out the best option. The goal was to offer large common spaces and smaller private rooms without compromising privacy and comfort, as well as avoiding waste and promoting a modular approach.
The rooftops, in a similar layout to the ground floors, each have two terraces and two co-working areas aligned with the vertical circulation blocs. At the heart of the floor is a mixed-use space, related to the commercial usage on the ground floor. On top of the market is a greenhouse, on top of the drugstore is a gym and of top of the daycare is a reception hall. These amenities would be available to all students, not only those living in the residences, to create a stronger sense of community.”
“I love that offsite construction and modular design, through architecture, is a way to express the celebration of modernity and technological advancements. A very large portion of the world’s carbon emissions comes from construction, and it is our duty, as designers of tomorrow, to act
ethically towards our planet and its occupants.”
—Sarah Samsoudin, part of this year’s second place-winning team from Université du Québec à Montréal
About the Author: John McMullen, PCM, is the marketing director for the Modular Building Institute. You can reach him directly at mcmullen@modular.org or on LinkedIn.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.