Making Sense of the Affordable Housing Crisis
According to a recent report called “The State of the Nation’s Housing 2018” issued by the Joint Center for Housing Studies of Harvard University (JCHS)
Homeownership rates among young adults are even lower than in 1988, and the share of cost-burdened renters is significantly higher, with almost half of all renters paying more than 30 percent of their income for housing. Soaring housing costs are largely to blame. The national median rent rose 20 percent faster than overall inflation between 1990 and 2016 and the median home price rose 41 percent faster. While better housing quality accounts for some of the increased costs, higher costs for building materials and labor, limited productivity gains, increased land costs, new regulatory barriers, and growing income inequality all played major roles as well. (jchs.harvard.edu/state-nations-housing-2018)
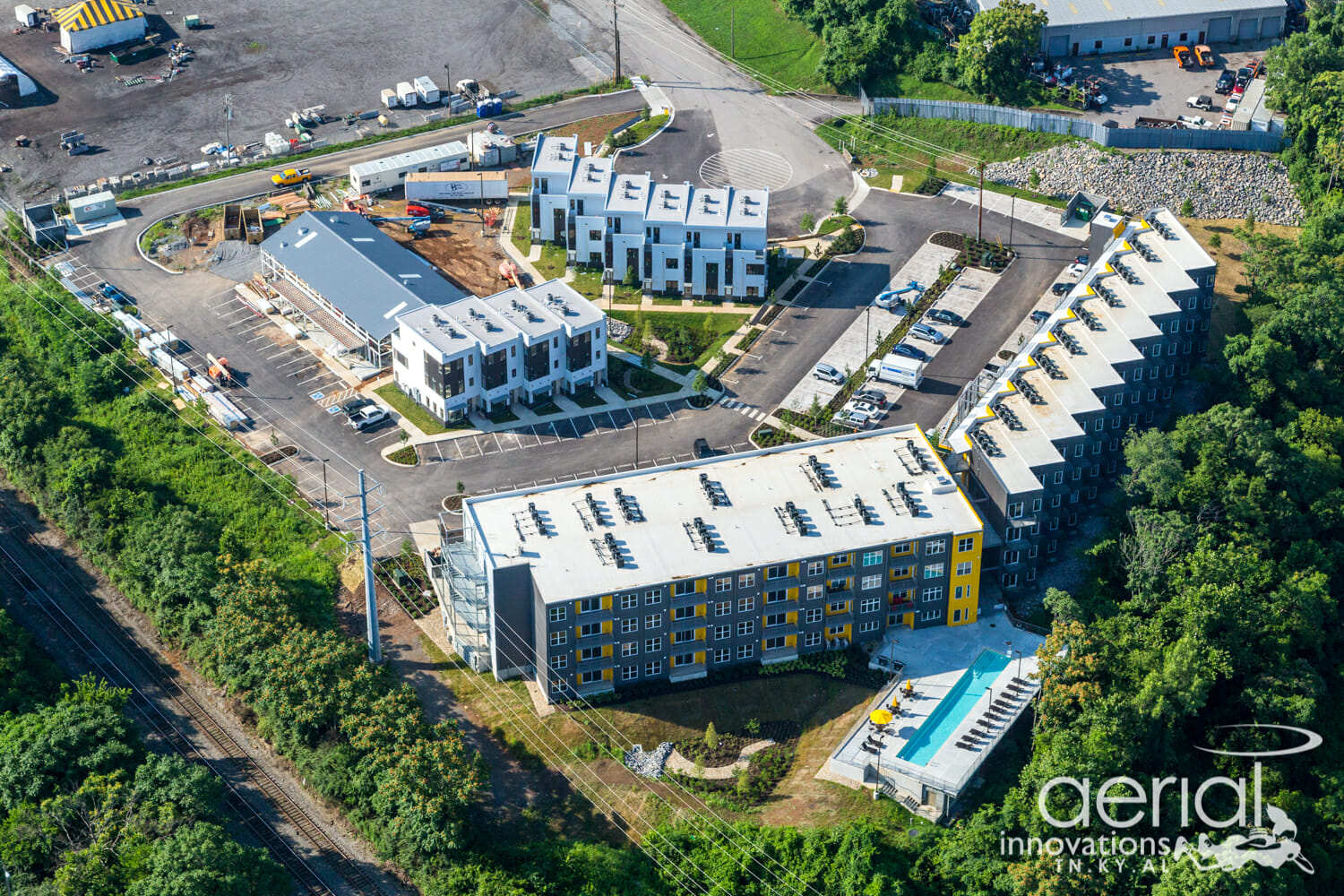

Four-story modular multi family complex in Tennessee / Source: Core Development and Aerial Innovations
And there doesn’t appear to be any relief in sight. In California alone, about 180,000 housing units are needed annually to keep pace with population needs, yet only about 80,000 housing units come online annually. In a recent New York Times article, it was reported that the federal government now classifies a family of four earning up to $117,400 as low-income around San Francisco’s Bay Area. To address affordable housing in the area, tech giant Google recently contracted with modular manufacturer Factory_OS to deliver 300 housing units to be used by Google employees.
Can modular construction help?
John Romanin of The Renter’s Lobby believes the nation has reached a crisis point. The Renter’s Lobby focuses on policies and legislation aimed at bringing a constructive new perspective to the housing policy debate. According to Romanin, “For the two decades between 1960 and 1980, 10 million apartments were built in the United States. Volume supply met demand at rental rates affordable to most American renters. By contrast, between 2000 and 2020 less than five million multifamily units will be built; with only 20% (or one million units) considered affordable. At the same time, renter household formation exceeded seven million new renters creating a shortfall of six million affordable housing units.”
What caused this supply shortfall and why aren’t more affordable housing units being built?
Romanin continued, “There are two reasons for the shortfall: The first relates to outdated, ineffective and terribly counter-productive National Affordable Housing and Housing Finance Policy. The second is the long-held private-sector misperception that affordable housing and management is not profitable nor sustainable without government subsidy."
Romanin is part of a newly formed group called the “Housing Crisis Solutions Coalition” (HCSC) which believes that advocacy and education programs can solve both problems by leading efforts to change policy and to demonstrate that Affordable Housing can be very profitable and rewarding.
The Coalition has set a goal of 10 million “affordable” units through 2038, or half a million units per year. “Only Modern Methods of Construction (MMC) can meet the technical demands of a scaled growth path on a cost-basis that can support this unique market," Romanin said. "Unsubsidized Affordable Housing development hinges on volume delivery of turnkey product-lines, community designs, and integration of production time efficiencies in all elements of the development and construction process."
“There are two reasons for the shortfall: The first relates to outdated, ineffective and terribly counter-productive National Affordable Housing and Housing Finance Policy. The second is the long-held private-sector misperception that affordable housing and management is not profitable nor sustainable without government subsidy."
The same story is playing out across North America. Chicago-based general contractor Skender Construction is going “all in” with modular construction by recently announcing they will be building a factory on Chicago’s southwest side.
In Vancouver, British Columbia, city officials have already approved about 500 temporary modular housing units, primarily to address homeless population. Modular multi-family facilities are also becoming more common in places like Boston, Philadelphia, and Seattle.
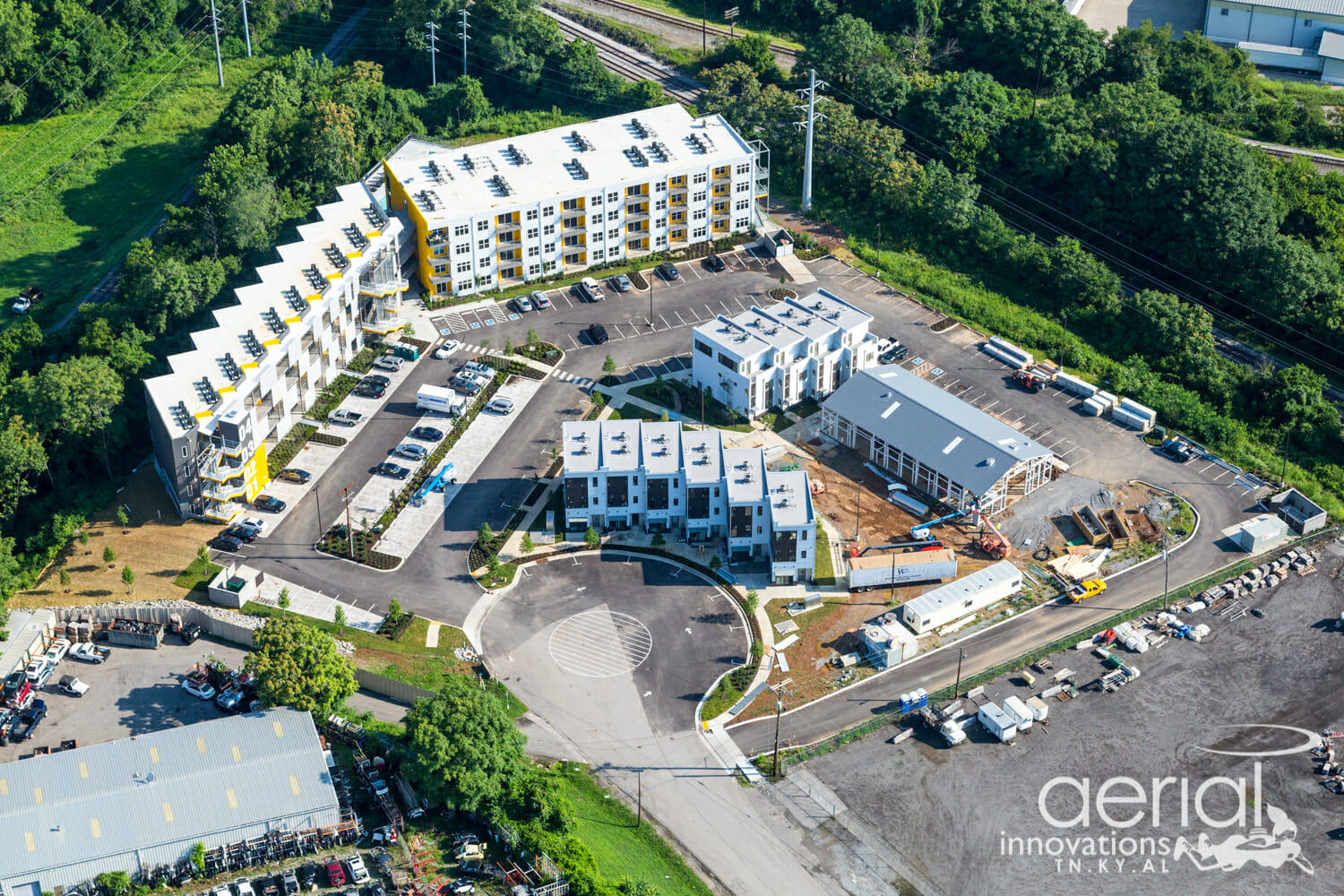

Four-story modular multi family complex in Tennessee / Source: Core Development and Aerial Innovations
What’s driving developers to modular construction now?
According to a recent article in Building Design and Construction Magazine, the number of residential construction workers is down 23% from 2006. Skilled trades like plumbers, carpenters, and electricians are down close to 17%. As a result, labor costs have risen about five percent a year for the past three years. Prefabrication, which is a more efficient way to build, may be the best hope to quickly build affordable housing, some industry insiders believe.
Chris Waters, then-Director of Business Development for Champion Commercial Structures, offers several factors including labor shortages, cost increases, schedule pushes, and quality. He adds “truly, the largest underlying factor may be predictability. In today’s environment, developers can predict very little or nothing in the way of cost control, the securing of labor, forcing schedule adherence, and ensuring a quality product. Either one, two, three or even all four can impact most every project today. With the modular scheme, as relates to a large portion of the project being built off-site, there is a sense of predictability for all four elements of cost, labor, schedule, and quality. The frontend planning process creates and ensures cost certainty very early in the stages, and well in advance of production. From the plant production side, the labor is ensured. Workers show up each day in climate controlled conditions to perform the same build tasks, day-in and day-out.”
MBI asked, given these advantages, and based on the 25 or so multi-family projects your company has completed, why aren’t more developers seeking this solution? Waters stated, ‘’It’s change. Not all people like change and, often, that is viewed as risk instead of progressive reward. We’ve been building the same way forever, and modular construction is a bit of a paradigm shift for many. It moves the planning process up and every stakeholder must understand that." Kent T. Campbell, Vice President of Core Development in Nashville, Tennessee has completed over 30 multi-family projects but only recently started utilizing modular construction, having completed two projects in this manner. He echoed some of the same factors cited by Waters. “Nashville is currently experiencing unprecedented growth. Trade and labor availability are stretched, and that’s resulting in rising costs, longer construction schedules, and reduced quality of the finished product. We look to modular for greater control in all three areas” Campbell stated. He added, “Finding qualified general contractors and subs who understand the modular process and scope of work has been the biggest challenge.
Brice Leconte, developer and founder of Colorado-based IUnit says the main drivers for his company are better quality, a more predictable schedule and the environmental benefits. Leconte’s company has completed three modular multi-family units including Eliot Flats, a 40-unit complex consisting of 350 square foot apartments. He went on to say that his biggest challenge now is finding the right GC and architect who are willing to get behind it (modular construction) and see it through.
For its part, HCSC is putting money behind their words. Modular industry building initiatives have begun with a first formal effort to demonstrate “Economical Housing by Design.” A Modular Affordable Home Living Community in Arizona, in its first phase, aims to build 550+ units to demonstrate the value of modular off-site construction for delivering unsubsidized affordable housing.
None of this is to suggest that modular construction by itself can address this massive shortage of housing. However, MBI sees no possible way to close the gap without greater adoption of industrialized processes such as modular construction.

Affordable Housing Project CHAMONIX in Vail, Colorado from Prefab Logic / Source: Prefab Logic
This article originally appeared in the Modular Advantage Magazine - Third Quarter 2018 released in September 2018.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.