The Key to Adaptable Smart Buildings is Less Construction, More Assembly

About the Author: DIRTT creates interior construction powered by technology. Prefabricated. Flexible. Fast. Sustainable. Solutions for the workplace, healthcare, education & more.

Smart buildings are more than tech-enabled structures.
They are living, connected ecosystems of architecture, design, and operational efficiency.
Done right, these ecosystems enable a truly connected environment — helping businesses improve both sustainability, as well as the health and well-being of their employees.
Of course, digital systems play a key role in connected environments. But tech alone isn’t enough to help a smart building adapt to future needs and tech advancement, says Paul Garner, market segment strategist at DIRTT.
“If the structure of a physical space doesn’t allow for adaptability, it can prevent an organization from fully realizing their sustainability and business objectives,” he says. “So we need to back up and rethink how we construct smart buildings in the first place.”
This is why a growing number of architects, contractors, and engineers are looking for alternatives to traditional construction methods.
They know that ending up with a smart building that can be adapted as needed, requires the initial construction process to be just as smart.
Smart Construction 101
“What if instead of constructing a building, we assembled it?” asks Garner.
Rather than building everything on-site from scratch as is traditionally done, smart construction streamlines the creation of key building infrastructure by having it designed and prefabricated beforehand at an industrial manufacturing plant.
Then, it just has to be transported to the building location and assembled.
This is not a new process for anyone who has followed modular construction, but the outcome of building internal space with modular components is adaptability, and that is one of the most sought-after attributes of space today.
With industrialized construction, not only does this make the building process more efficient and require less labor (saving time and expense), but since all the prefabricated components are modular, you end up with a structure that is intentionally designed to be adaptable.
The design part of the smart construction process relies on digital tools to map out exactly what a client wants their future smart space to achieve, says Garner.
“It’s often dependent on advanced design tech such as building information modeling (BIM), which enables clients to pick and choose every detail of a custom interior space using virtual or augmented reality.”
The prefabricated walls, flooring, panels, sub-assemblies and critical services (such as electrical and network cabling) are manufactured, which makes them easy to assemble when they are first installed, and flexible enough to be re-assembled in future.
“You are not only maximizing productivity through lean manufacturing, you are increasing user benefits by creating spaces that can adapt and remain relevant over time,” Garner says.
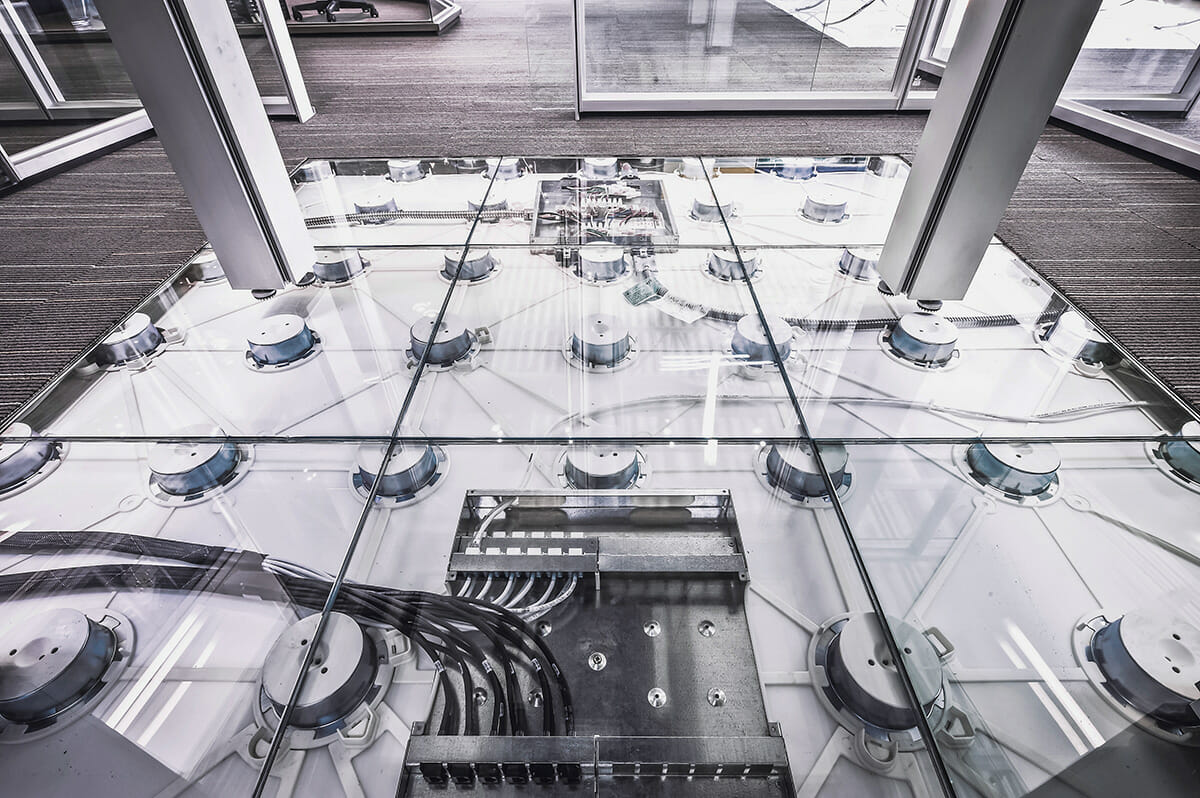

Enable Power and Tech Adaptation with “Connected Infrastructure”
Adaptability is integral not just for visible interior elements like walls and floors, but also critical services infrastructure such as cabling assemblies, electrical, and low-voltage networking cabling.
This is true for all structures, but especially smart buildings that heavily rely on these services to enable a connected environment featuring automation, insight, and more.
“The traditional approach to both installation and reconfiguration of such infrastructure is time-consuming, prone to faults and messy — plus it requires highly-skilled labor, which is increasingly hard to come by,” says Garner.
The modular solution that fixes these challenges is what DIRTT calls “connected infrastructure.”
Electrical build-outs are a good example of this.
On a standard construction project, tradespeople painstakingly set up branch wiring and device connections. It’s a slow and inefficient process that also leads to a lot of material waste, because cabling is measured and cut on-site.
But a connected infrastructure approach utilizes modular cabling, virtually eliminating these problems. “Digital design technology ensures that these manufactured cables are perfectly cut to size at the factory — so there’s less waste,” Garner says.
Additionally, the cables easily click into place thanks to conversion points that transition conventional power for modular use. It’s just plug-and-play, essentially.
Meanwhile, the cables are easily accessible during the installation process beneath or behind modular walls and floors. So there’s no need to demolish, drywall and repaint.
“This all happens without major construction taking place. And in most cases, without having to engage an electrical contractor,” Garner concludes.
Install is nimble, adaptation won’t disrupt regular use of the space, and environmental waste is reduced.
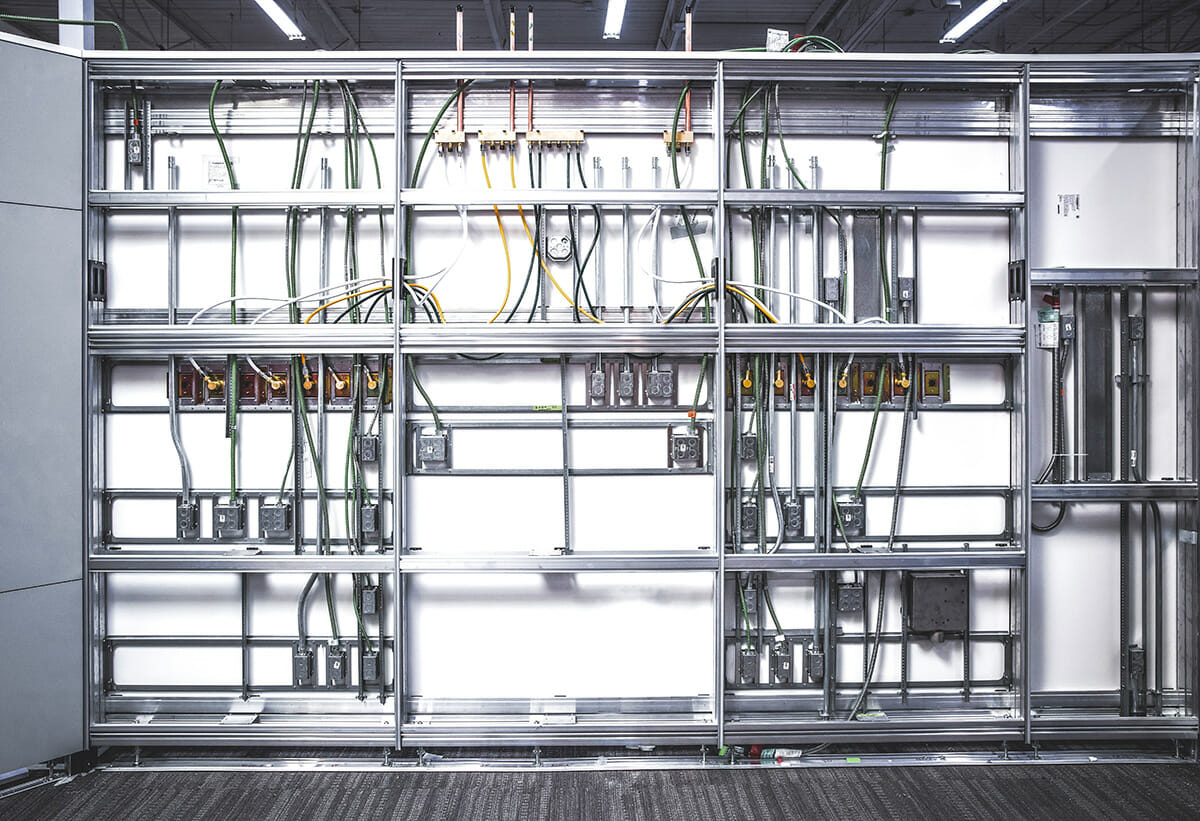

Enable Power and Tech Adaptation with “Connected Infrastructure”
The environmental impact of traditional construction is also driving change in the industry — and interest in smart construction.
“The sheer volume of waste generated by construction can’t be ignored,” says Garner.
Fortunately, the smart construction combo of digital design tools and manufactured products reduces waste in seven key areas: overproduction, transportation, motion, waiting, processing, inventory, and rework.
Most of those provide immediate sustainability benefits. But there’s an intrinsic tie between sustainability and adaptability as well.
“The more adaptable to change we can make our spaces, the more efficient we can be when that change comes,” Garner explains.
And since you’re often able to repurpose modular components, there’s less raw material demand too, which lessens environmental impacts throughout the building’s life cycle.
“This efficiency translates to lowered costs for maintenance and renovation, and a reduced carbon footprint overall,” says Garner.
Though we’ve seen smart building technology play a pivotal role in accelerating the efficiencies of in-building management systems, that dedication to sustainability needs to start earlier, and play a role in every step of a construction project.

Connected environments enable the health and well-being, and productivity of employees
Smart construction, and especially connected infrastructure, positively impact both the efficiency of your building’s operations and the experience of your employees who occupy the space — which in turn improves your business as a whole.
“The return on investment for smart buildings isn’t just quantified financially by energy savings or less waste. It is a more complex formula including elements such as employee productivity,” explains Garner.
For instance, reconfiguration of a space is often required to re-calibrate occupants within their work environments over time.
And when users ask for workplace adaptation to support their specific needs, this is easy to achieve thanks to the speed and certainty enabled by manufactured infrastructure.
“Because of adaptable components, reconfiguration is quick and fluid, allowing the space to be personalized, as well as creating a more productive and inviting workplace,” says Garner.
Those changes can be made with little disruption to the workforce, and occupants’ exposure to harmful off-gassing from paints and adhesives is reduced or even eliminated due to off-site construction and thoughtful material selection.
An organization’s biggest, most important investment is its people, and the ecosystem that’s enabled by smart construction helps occupants stay safe, comfortable, and productive.
Choose smart construction to optimize your smart building ecosystem
The building industry is perfectly positioned to take advantage of smart construction right now. Everyone from designers to fabricators are embracing digitization — and smart construction methods clearly optimize both the build phase and future configuration.
“This allows us to get it right the first time,” Garner says. “As manufactured construction is adopted more widely, it will help address declining productivity and wasteful processes in the world of construction.”
Meanwhile, the foundational benefits of smart construction approaches (and connected infrastructure in particular) enable real gains in adaptability, sustainability, and the health and wellbeing of occupants.
“It’s time to make assembling, rather than construction of our indoor ecosystems, the norm, not the alternative,” Garner concludes.
Learn more at DIRTT.com.
More from Modular Advantage
How Stack Modular Is Using AI to De-Risk Mid- to High-Rise Modular Construction
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept in modular construction—it is already reshaping how complex buildings are evaluated, designed, and delivered.
Gearing Up for the 2026 World of Modular
The Modular Building Institute (MBI) is bringing its global World of Modular (WOM) conference and tradeshow back to Las Vegas in April, and with it comes some of the industry’s best opportunities for networking, business development, and education.
New High-Rise Modular Apartment in Abu Dhabi Points Toward the Future of Multifamily Construction
Eagle Hills International Properties chose the BROAD Holon Building for a 16-story market rate apartment building in Zayed City, a central business district of Abu Dhabi. The project highlights the potential of the Holon system of volumetric modular construction to accelerate housing delivery.
MBI Announces First Ever Industry Apprenticeship Program in Collaboration with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center
MBI recently agreed to partner with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center (MAMC) to provide bona fide USDOL-approved apprenticeship programs for the industry.
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.