Innovating in Modular Construction: BROAD's Holon Building

Jeremy Zimman is the director of communications at BROAD U.S.A.
The BROAD Group was founded in China in 1988 and incorporated in the US in 1997. Its flagship product has been high-capacity HVAC systems for commercial and industrial use, and for residential towers. Since 2005, they’ve also manufactured air purification, ventilation, and filtration systems. The move into modular construction was made in 2009, when the company’s Chairman, Zhang Yue, founded BROAD Sustainable Buildings (BSB).
BSB’s factories are all in Changsha, which is in Hunan province in South China. “We came to modular construction from a background in high-volume manufacturing,” says Jeremy Zimman, Director of Communications at BROAD USA. “We have a highly automated production line which presently turns out 22,000 square feet per day, and we’re soon going to expand to 110,000 square feet per day.” The company moved into modular construction to address deficiencies in the construction industry. The first objective was to speed up the construction project cycle. “The BROAD Holon Building is 100% factory made, which is more than 20 times more efficient than on-site construction. The number of workers can be reduced by more than 70 percent, which greatly reduces labor costs and improves capital turnover,” Zimman says.
The company also set out to reduce steel consumption, improve material strength, and minimize carbon emissions. “From the beginning, we avoided the use of concrete in modular buildings. The manufacture of concrete emits a huge amount of greenhouse gases,” Zimman says. “The use of environmentally-friendly stainless steel will cut CO2 emissions dramatically.”
In addition to reducing emissions due to construction processes and materials, Zimman notes the importance of reducing emissions during each building’s operation — by increasing its service life and reducing its energy consumption.
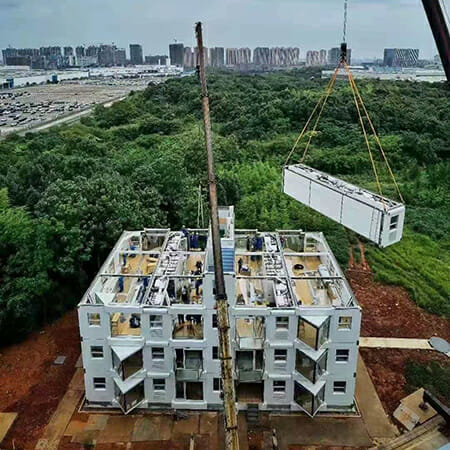

BROAD’s future is very much focused on their Holon Building concept. These mid-rise and high-rise residential buildings feature a repeatable modular design. Each module is the size of a standard 40 HQ [high cube] shipping container — so they can be transported like regular containers. On site, they fold out to 16 feet wide.
“The BROAD Holon Building is constructed of stainless steel which is 95 times more resistant to corrosion than carbon steel and therefore has an infinite lifespan. The exterior walls use 8.5 inches of rockwool for thermal insulation, which is equivalent to a concrete wall with a thickness of 30 feet, and the building comes with exterior sunshades and interior thermal shades, 3- or 4-pane glass windows, and a fresh air heat recovery system,” Zimman explains. “This reduces energy consumption by 80 to 90 percent, which translates into 440 lbs/m² of carbon reduction per year.”
Another important reason driving BROAD’s involvement in the construction industry is that in 2008 there was a terrible earthquake in Sichuan Province, which is not far from the company’s home base in Hunan Province. “Many tens of thousands of people lost their lives. BSB was founded to develop buildings to withstand up to magnitude 9 earthquakes.” Zimman says that goal was achieved with their first building in 2010. Since then, the company has continued to innovate. In 2017, they developed B-CORE, their stainless steel structural material, which all their modular buildings are now built with.
What is B-CORE?
Zimman explains that “B-CORE is hardened with a hot-air copper brazing process at 2012°F. We developed the ovens ourselves — through ten different iterations and with many failures along the way. Overall, we invested $1.25 billion over the last 12 years to get to where we are today with B-CORE.” B-CORE has a sandwich structure — stainless steel plates connected by stainless steel tubes. The thickness of the plates and the tubes varies depending on the application, such as floor slabs or exterior walls. “What doesn’t change is the sandwich structure which makes it much lighter, yet much stronger, than carbon steel. 1 ton of B-CORE slab-sandwiched stainless steel is equivalent to 4 tons of carbon steel.”
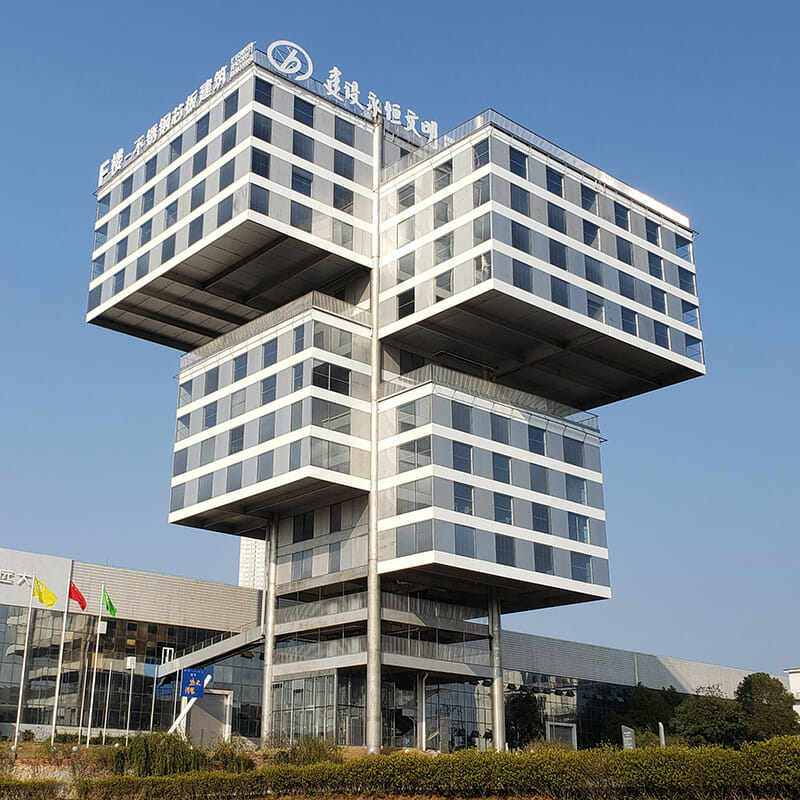
The company’s administrative building — which they call the F Building, because it’s shaped like the letter F — was built using B-CORE in Changsha, China at the end of 2019. “This material enables us to do amazing things,” Zimman says. “The F Building has a 55-foot cantilever, due to the lightness yet strength of B-CORE. The entire 81,000 square foot building is supported by just four one-meter-wide B-CORE pillars.”

Related Reading:
B-CORE: The Modern Material from BROAD
In this article—which originally ran in the Nov/Dec 2021 issue of MBI's Modular Advantage magazine—Sunny Wang, general manager at BROAD USA, and his colleagues, Tony Sun (a structural engineer at BROAD) and Jeremy Zimman (BROAD USA’s Director of Communications), share some of the details about B-CORE, a strong, lightweight stainless steel material it invested over a decade and $1.25 billion to develop.
NPI Hospital in Seoul
Zimman explains that in the US during the pandemic, “There were NPI [negative pressure isolation] rooms in converted hotels and other buildings. But if there’s central air conditioning and spaces under the doors, it’s very difficult to maintain negative pressure. With a purpose-built, airtight room, with its own dedicated HVAC system, you can more effectively prevent cross-contamination.”
Last year, using their B-CORE stainless steel material, BROAD manufactured NPI rooms for treating COVID patients at the Seoul National University Hospital in South Korea. BROAD supplied the NPI rooms turnkey, including the NPI systems, HVAC, BROAD’s own ventilation and air purification systems — everything except the clinical equipment. From contract to completion, the whole project took 23 days, and the on-site installation was completed in only 2 days.
“These turnkey NPI rooms combined all our core competencies and expertise in modular construction, HVAC, and air purification,” Zimman says.
The Holon Building Concept
Zimman says that BROAD’s future is very much focused on their Holon Building concept. These mid-rise and high-rise residential buildings feature a repeatable modular design. “Each module is the size of a standard 40 HQ [high cube] shipping container: 40 feet long, 8 feet wide, 10 feet high — so they can be transported like regular containers. On site, they fold out to 16 feet wide.”
When using modular construction, Zimman explains that cost- and time-savings increase when more of the construction process is completed in the factory. Quality control also improves. All the mechanical, electrical, plumbing, and interior fixtures are integrated into the Holon Building modules at the factory.
“On site, we just unfold the modules, bolt them together, and connect the utility hookups. The building is then move-in ready,” Zimman says.
Holon Buildings are designed for maximum flexibility. “The floor plan and room layout can change any time after construction is completed. Even the height can change — we can just pop off the roof module and add more floors. The buildings can be repurposed, and even dismantled and relocated,” Zimman says.
The first example of a BROAD Holon Building, the Garden A-1, was built in Changsha in June of this year. The 11-story, 32,000 square feet apartment building is comprised of 56 modules, which were manufactured in 15 days and stacked on-site in under 29 hours.
Zimman describes the company’s 1000 City Strategy: “We intend to put Holon Buildings in 1000 cities, including 80 in the US in the next eight years. They’ll be mixed use facilities with offices, and residential rental on the upper floors, and community spaces on the lower levels. This is in addition to supplying Holon Buildings to developers and real estate investors.”
If you’d like to learn more about BROAD, Zimman notes that the company will be exhibiting at the Offsite Construction Expo in Denver in September and will also have a speaking slot on the virtual show.
About the Author: Zena Ryder is a freelance writer, specializing in writing about construction and for construction companies. You can find her at Zena, Freelance Writer or on LinkedIn.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.