Maximizing Modular Design and Construction to Create Affordable Housing

About the Author: Nick Gomez of Lowney Architecture has more than 15 years of experience working on multi-family housing and modular projects for nonprofit and for-profit clients. As the Oakland, Calif.-based firm’s Multi-family Studio Director, Nick has managed award-winning projects from design development through construction administration.
Volumetric modular design and construction can save time and money and create affordable, healthy housing. However, there are many ways this delivery method can go awry. By starting with the assumption that every building design is modular and then seeking to eliminate it, a project will employ the best delivery method for its circumstances. Lowney Architects completed its first modular multifamily project in San Francisco in 2013 and has since worked on over 60 multifamily and hotel projects totaling over 5,300 unit/keys. Clients include the factories themselves, market rate developers and LITC financed developers sponsoring affordable and supportive housing projects. Modular projects open up a world of possibilities, but also have pitfalls. Following are ways to optimize projects with buildings constructed offsite and how common pitfalls can be avoided.
Site selection is key.
Modular buildings are built with volumetric boxes that are craned onto the site-built foundations. Site access and staging areas are critical to identify, at least provisionally, upfront. There should be few, if any, aerial obstructions to make craning the boxes easier as the site’s geometry can limit the viability of this delivery method.

Pie shaped or irregularly shaped sites do not lend themselves to efficient layout of rectangular boxes. These sites should be eliminated; flat, rectilinear, sites that have dimensions close to multiples of the intended box sizes (up to 15’-10 x72’) are preferred. Zoning designation is also a critical factor in site selection. Most modular buildings are one foot taller per floor than their site-built alternative. Often modular buildings will not fit within the site’s zoning envelope because the zoning codes did not anticipate modular construction (check allowable building height first!). The lesson here is, don’t force it. Some sites are just not suitable for modular construction.
Keep every project modular possible for as long as possible.
It is far easier to “demodularize” a project than to redesign a site-built project to conform to the requirements of a factory. Become familiar with factory-built construction and understand the opportunities and limitations before designing. Keep a building organization simple, such as double-loaded corridors with walls that track across corridors in plan. Repetition is important but should not limit design. Always be clear about and evaluate what is the factory scope and what is the site scope; never confuse the two and constantly seek clarity as the design process unfolds. Try to work with SMEP engineers who have experience with modular and consult with them. Review exterior façade articulation and modular box stacking. Pay attention to vertical shaft layouts and exterior exhaust runs. Importantly, reach out to your preferred factory for input on constructability, module layout, and their scope in the overall project.
Design decisions are front-loaded in modular projects.
The good news is that this reduces the likelihood of change orders. The bad news is that this design process is vastly different from conventional site-built projects and can confound unsuspecting clients (and their teams). All decisions that the factory will act on - from structural issues to window locations to interior finishes and equipment - must be procured by the factory and installed in the module sometimes before a foundation is poured. Thus, the importance of “design freeze,” so that the factory can efficiently manufacture its modules.
Modular projects cost more to design than site-built projects, even though they cost less to build.
This is not only a result of the front-loaded design decisions process, but because modular projects typically require two building permits and, therefore, two drawing sets to get approved. The modular drawing set is approved by the state, the site scope is approved by the local municipality. Again, be clear on who is providing what (factory or GC) and who is reviewing what (state or city). This must be explicit in the drawings. Always have one team of professionals working on both drawing sets. Never have two teams working on the two separate drawing sets as this will result in confusion and items not getting fully coordinated. It is often beneficial to hold a brief explanatory seminar with novice city officials to help them understand what is modular design and construction, and more importantly, what their scope of review is. Cities, at times, can overstep their review scope, which delays projects and, in some instances, adds cost.
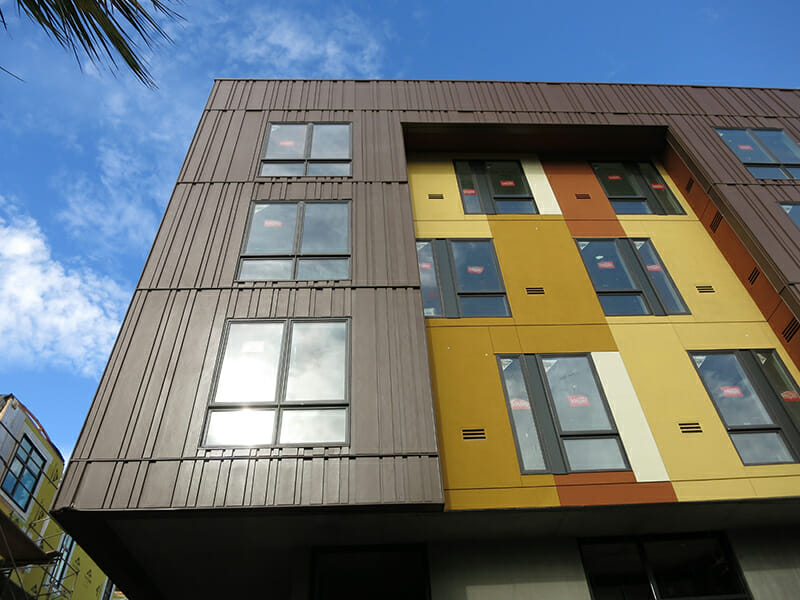
Modular is beautiful. But you must make it so.
Just because a building is manufactured in a factory does not determine it appearance. A modular building can assume the trappings of any architectural style if you respect factory optimization. The Mayfair mixed-use project in Albany, California pushes the limits of this last axiom. The City required the project to conform to its approved guidelines, which required a high degree of architectural expression that included building reveals, a “super portal”, and a muscular façade articulation. The result was done with a high degree of structural, factory and client coordination.
If the conditions are right, modular can be right.
Always seek to disprove the viability of modular against its site-built option. The further along in the design and construction process you go, the more expensive it is to change the project delivery approach.
It is becoming increasingly clear that the archaic construction approach deployed to solve today’s housing crisis is not up to the task. There are better ways to build affordable, decent housing. Modular is one way to do so.
Nick Gomez has over 15 years of experience working on multi-family housing and modular projects for both nonprofit and for-profit clients. As Director of Lowney Architecture’s Multi-family Studio, Nick has managed award-winning projects from design development through construction administration. To evaluate modular solutions for your project, Nick can be reached at nick@lowneyarch.com or 510.269.1107.
This article was first published in the Modular Advantage - November/December 2020 Edition.
More from Modular Advantage
How Stack Modular Is Using AI to De-Risk Mid- to High-Rise Modular Construction
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept in modular construction—it is already reshaping how complex buildings are evaluated, designed, and delivered.
Gearing Up for the 2026 World of Modular
The Modular Building Institute (MBI) is bringing its global World of Modular (WOM) conference and tradeshow back to Las Vegas in April, and with it comes some of the industry’s best opportunities for networking, business development, and education.
New High-Rise Modular Apartment in Abu Dhabi Points Toward the Future of Multifamily Construction
Eagle Hills International Properties chose the BROAD Holon Building for a 16-story market rate apartment building in Zayed City, a central business district of Abu Dhabi. The project highlights the potential of the Holon system of volumetric modular construction to accelerate housing delivery.
MBI Announces First Ever Industry Apprenticeship Program in Collaboration with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center
MBI recently agreed to partner with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center (MAMC) to provide bona fide USDOL-approved apprenticeship programs for the industry.
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.