How Climate Change Will Impact Existing Fleet Units – Brace Yourself!

Tom Hardiman, CAE, is the Executive Director of the Modular Building Institute.
Several years ago, MBI worked with the ICC to get language included in the International Building Code to protect existing fleet assets from having to be brought up to new codes upon relocation. Many code officials applied the “moved structures” section of the IBC to fleet units being relocated.
MBI worked to eliminate the “moved structures” section completely form the IBC and added a new section (3113) specific to relocatable buildings. That section of the code, included in the 2018 IBC, makes it clear that any newly constructed relocatable building must comply with the code for new construction. However, any existing building, one for which a permit has been pulled, is governed by Chapter 14 of the International EXISTING Building Code (IEBC) not the IBC.
General contractors, new to modular construction, were on the hunt for presentations that might help answer questions about how to efficiently and effectively get started in the offsite industry. The Lounge proved to be a fruitful space to connect GC’s with other organizations to teach, learn, and collaborate. If we want to grow our industry we need to consistently create easily accessible training resources and make sure we are making space for this type of learning at offsite conferences.
Pittsburgh-based Module has been working on training standards since their launch of the Last Mile Network that includes the manufacturers, architects, transporters, and GC’s who are trained on the MODULE building system. The resulting training manual, the Off-Site Construction Playbook, includes sections on Design & Pre-Construction, Site and Set Day Prep, On-Site MEP Connections and Completion, and Post-Set On-Site Finish Work. Module is now helping other companies create their own Playbooks.
In summary, Chapter 14 states that any building relocated into an area must comply with the applicable site conditions, namely wind, snow, seismic, and flood hazards. By including this “grandfathering” provision for existing fleet, MBI has been able to protect these assets and allow them to continue to be used, so long as they meet the local site conditions.
This rarely has posed any issues for our industry, because how often do wind, snow, and seismic requirements change after all? Well….as it turns out, some jurisdictions are looking at their site requirements due to the impact of climate change on buildings. Here’s a few ways climate change is impacting existing building inventory:
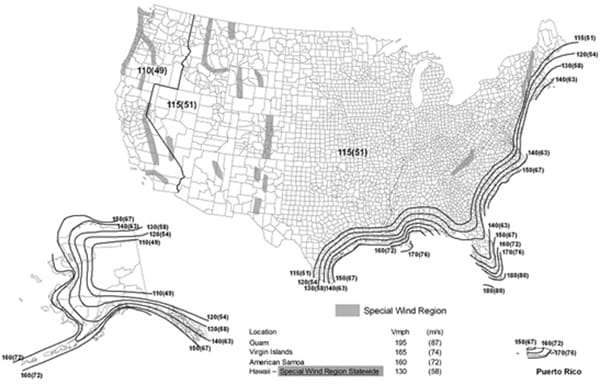
2015 IBC 1609.3 Ultimate design wind speed.
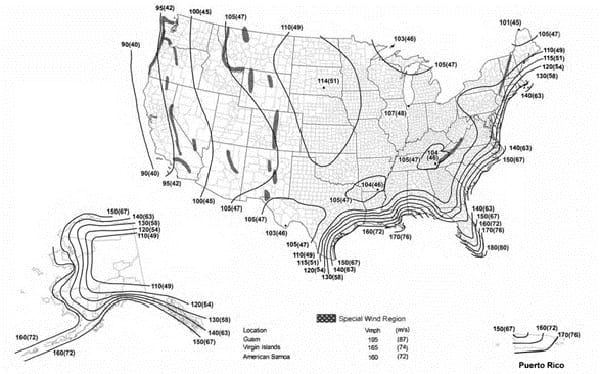
2018 IBC 1609.3 Basic design wind speed.
- Higher temperatures can lead to increased cooling demands, which can strain HVAC systems and lead to higher energy, maintenance, and / or replacement costs.
- Stronger storms, hurricanes, and floods can damage building exteriors, foundations, and infrastructures like drainage systems. This can lead to more frequent repairs and higher maintenance costs.
- Increased precipitation and humidity can lead to issues like mold growth, rot, and deterioration of building materials as well as impacting indoor air quality and occupant health.
- In regions where temperatures fluctuate around the freezing point, more intense freeze-thaw cycles can cause cracks in foundations, walls, and pavements, leading to structural damage.
- As climate patterns shift, buildings may need retrofitting to improve energy efficiency, such as better insulation or updated HVAC systems, to address the changing climate.
- Increased risks from climate change can lead to higher insurance premiums and property devaluation, affecting the economic viability of maintaining certain buildings.
In reviewing the design wind speed map in Chapter 16 of the IBC for example, the requirements changed from the 2009 version and the 2012 code and again from the 2015 version to the 2018 code. To add to the confusion between 2015 and 2018, the terminology changed as well, from “ultimate” design wind speed to “basic” design wind speed. A handy conversion chart was also included in the codes to help “simplify” things between the two wind speeds.
In some areas, the requirement increased while other regions saw a decrease in wind design requirements. In fact, most areas of the country did see a decrease in wind speed design criteria based on the latest available data.
As an industry, we cannot expect the site requirements to remain unchanged over long periods of time, encompassing multiple code cycles. It is critically important for owners to follow potential building code changes relative to these site-specific conditions as it could impact all existing units labeled and weaken our “grandfather” provision. Remember, our code language protects only the box, not the site.
More from Modular Advantage
How Stack Modular Is Using AI to De-Risk Mid- to High-Rise Modular Construction
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept in modular construction—it is already reshaping how complex buildings are evaluated, designed, and delivered.
Gearing Up for the 2026 World of Modular
The Modular Building Institute (MBI) is bringing its global World of Modular (WOM) conference and tradeshow back to Las Vegas in April, and with it comes some of the industry’s best opportunities for networking, business development, and education.
New High-Rise Modular Apartment in Abu Dhabi Points Toward the Future of Multifamily Construction
Eagle Hills International Properties chose the BROAD Holon Building for a 16-story market rate apartment building in Zayed City, a central business district of Abu Dhabi. The project highlights the potential of the Holon system of volumetric modular construction to accelerate housing delivery.
MBI Announces First Ever Industry Apprenticeship Program in Collaboration with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center
MBI recently agreed to partner with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center (MAMC) to provide bona fide USDOL-approved apprenticeship programs for the industry.
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.