A Village Inspires a New Modular Emergency Housing Concept

Nathan Young is the CEO and Principle Builder at Oregon-based MODS. MODS works with homebuyers, architects, developers and nonprofit organizations to create high-quality, sustainable buildings. In this article, he discusses his company's new idea for emergency and transitional housing.
Transitional housing is temporary accommodation for people transitioning from homelessness into permanent supportive housing. Typically, the goal is for residents to move into permanent housing in less than two years — but to have a stable roof over their heads and support services on site in the meantime. St. John’s Village is a transitional housing community that opened in early 2021 in Portland, Oregon. It consists of 19 individual sleeping pods in the style of tiny homes, each with a twin bed, electric heating and lighting, storage space, and its own locking front door. On the same site, there are also communal buildings that include showers, laundry facilities, a kitchen, a dining room, and offices for support staff.
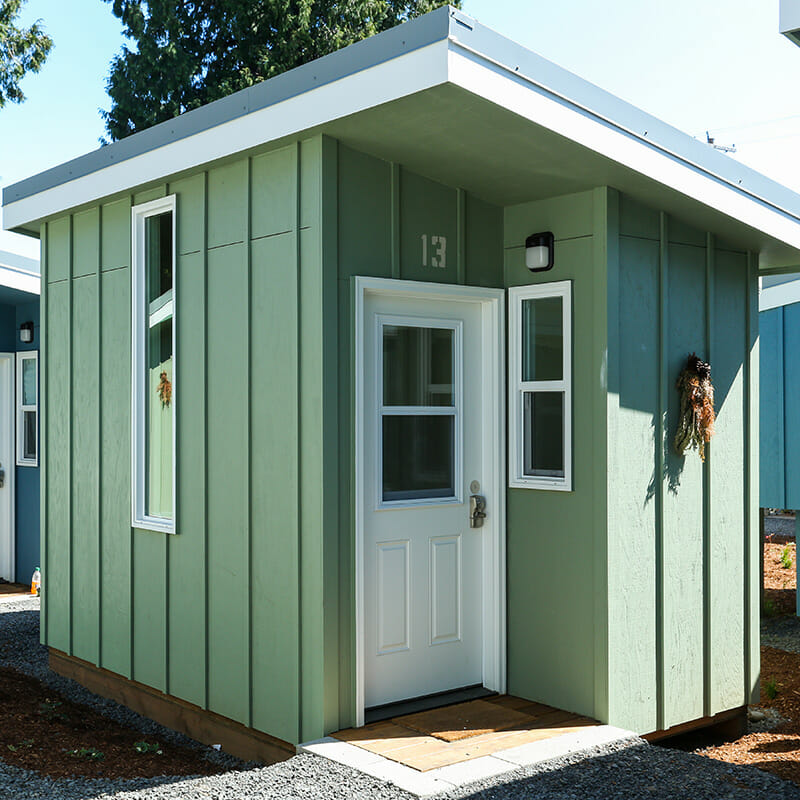
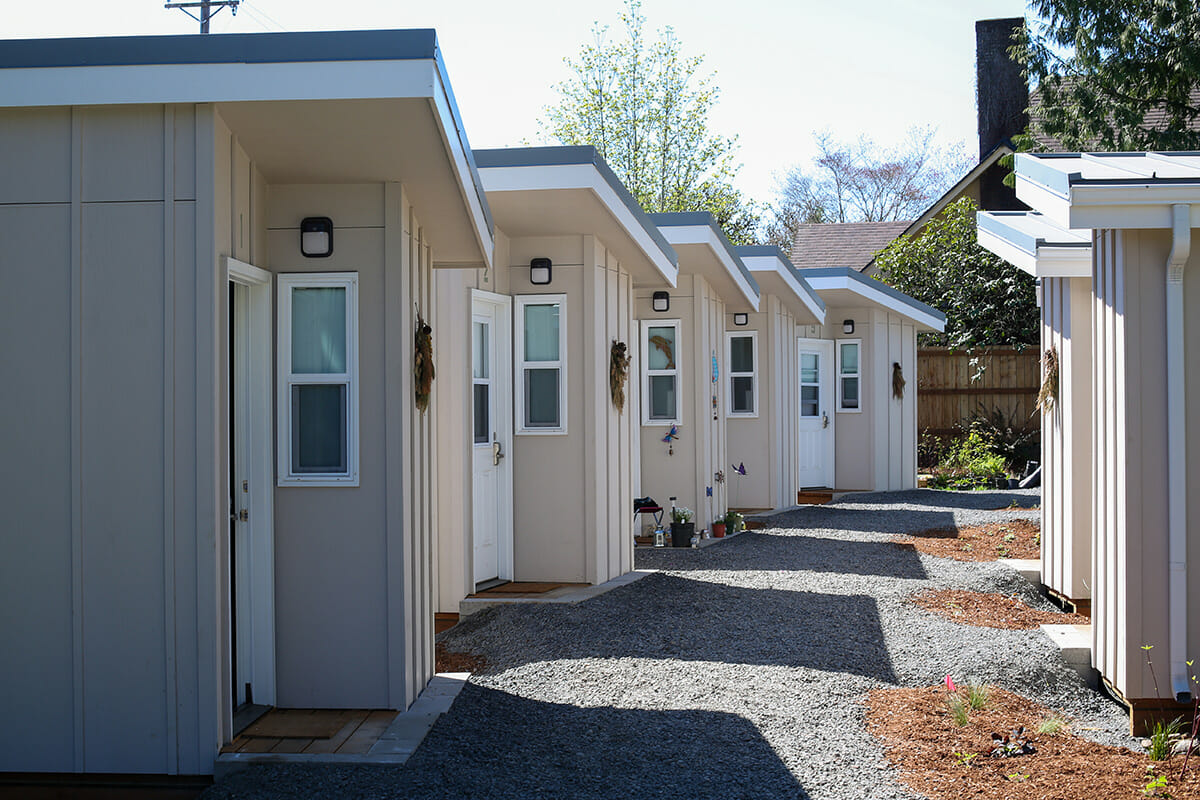


St. John’s Village is a transitional housing community that opened in early 2021 in Portland, Oregon. It consists of 19 individual sleeping pods in the style of tiny homes.
The buildings were constructed by Portland-based modular manufacturing company, MODS PDX. Nathan Young, CEO and Principal Builder at MODS, says that he and his team learned a lot from this project. “It’s not cost-effective to build individual pods,” says Young. “These ones ended up in the range of $30,000 each, which is generally not affordable for non-profits and municipalities who want to build this kind of housing.”
As well as not being cost-effective, Young says it’s also not efficient to build individual pods. “For example, you have to install electrical infrastructure on each individual pod instead of installing one electrical panel that can serve three to six sleeping pods. My guys basically said they’d never build another one of those again,” Young says with a laugh.
Towards More Efficient and Cost-Effective Villages
So Young teamed up with design partner, Kegan Flanderka, Principal at Base Design + Architecture to brainstorm what worked well, and what could be improved upon for future emergency and transitional housing projects.
“We talked with service providers who run these types of communities and they really like the village concept, with pods that can be placed in different configurations depending on the site,” Flanderka says.
The partners also received feedback that the village concept is important to the residents themselves — who typically want to move away from apartment block structures that can feel institutional. “It’s hugely important for the residents to have their own front door, and to have easy access to the outdoors,” Flanderka says. He also suspects that small village-type communities are likely to meet with less neighborhood resistance than larger apartment buildings.
“So, we wanted to keep the flexibility of the village concept,” Flanderka says. “But along with that flexibility, we also wanted something that was more efficient to build than individual pods.”



In the St. Johns Village, office, bathroom, and kitchen modules all match the same platform as the sleeping pods. The modules can range in length from 24 feet to 48 feet.
Having modules that contain more than one pod means fewer exterior walls, fewer roofs, fewer electrical panels, and so on, thus reducing the amount of materials needed for the same square footage. “It’s also more efficient to transport and install one module that contains three sleeping pods than three individual sleeping pods,” Young adds. Three individual sleeping pods also take up more lot space than three pods of the same size inside one module — a more efficient use of the available land.
The Emergency Housing Concept
Based on the experience with St. John’s Village and the information they subsequently gathered, Flanderka and Young developed their Emergency Housing concept, which has a variety of different modules that can be built on the same platform. So a single module can consist of three, four, five, or six sleeping pods. Office, bathroom, and kitchen modules all match the same platform. The modules can range in length from 24 feet to 48 feet.
“So, the same basic module can contain sleeping pods, or bathrooms, or we can take out the walls and turn it into a communal kitchen or a community room. Or we can leave in the walls and make offices,” says Flanderka. “By combining different configurations of the modules, you essentially get that same village idea.”
The Oregon Home Builders Foundation (HBF) was one of the partners working on the St. John’s Village project. It’s a non-profit
organization that facilitates renovating and building housing for the homeless, and Young says the organization is enthusiastic about the Emergency Housing concept. “We’ve now built a prototype module containing three sleeping units and have showcased it at various events organized by the Portland Home Builders’ Association,” Young says. Despite the sometimes slowly turning bureaucratic cogs at municipalities and non-profits, interest has been increasing.
“In addition to the City of Portland reaching back out to us, we’ve had some interest from Clackamas County, Hood River, and some outlying areas that are looking into it for housing the homeless and also for wildfires and other emergencies,” Flanderka says.
The west coast of the United States has a large homeless population, and the partners envision their Emergency Housing being placed anywhere in the area they’re able to service — from Seattle to Los Angeles. And, because they’re built to standard building codes, permitting depends just on occupancy and how the jurisdiction wants to treat them, based on zoning and density. “They could be permitted as congregate living or as apartments. If they’re on trailers, they’re temporary structures and
don’t need to go through the typical permitting process. We can work with the needs of each jurisdiction to permit them and make them legal structures,” Flanderka says.
A Virtuous Circle
The Emergency Housing modules have been designed so they don’t require highly skilled labor to build them — which opens up employment opportunities for the future residents of the buildings.
“We learned from talking with service providers that 10% to 20% of homeless people would be capable of starting work fairly quickly if only they had a roof over their heads and an opportunity,” Young says. So he and Flanderka have been working with HBF on a workforce training program to try to integrate the Emergency Housing into that program.
Young says, “If the people who live in them can help build them for the next group of residents, that’s a really good virtuous circle.”
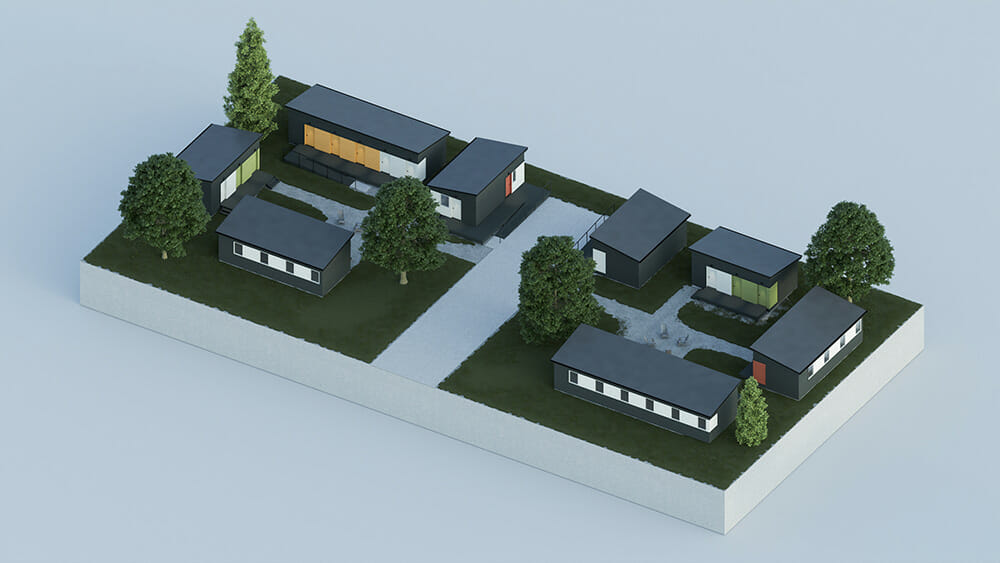
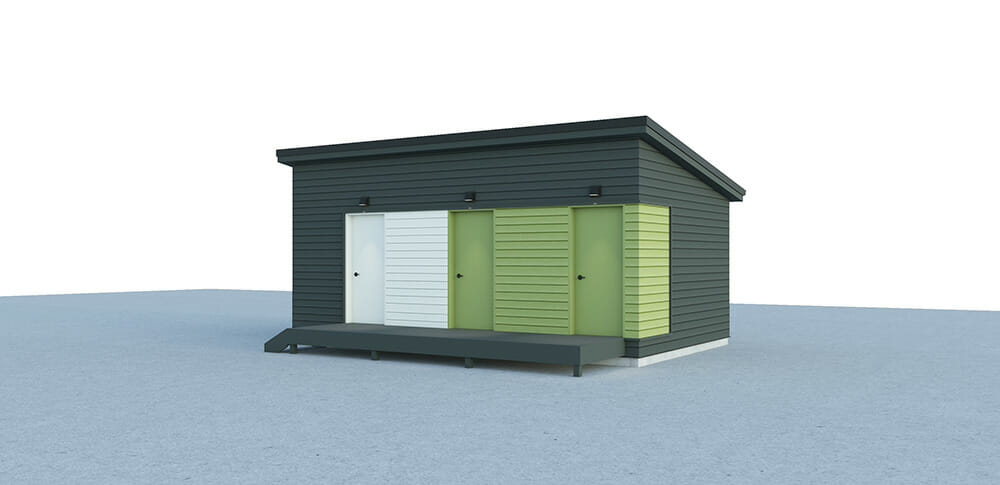
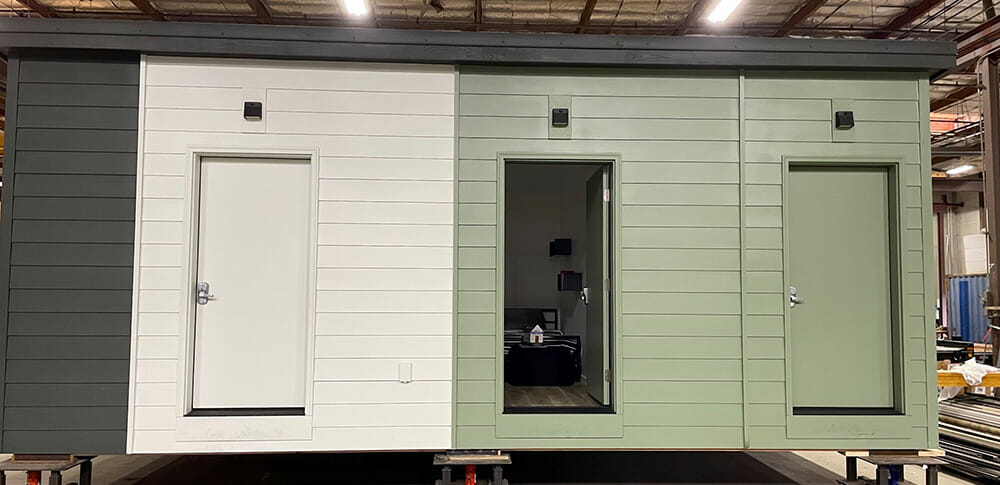



Computer renderings and finished prototypes of MODS’ emergency housing units.
About the Author: Zena Ryder is a freelance writer, specializing in writing about construction and for construction companies. You can find her at Zena, Freelance Writer or on LinkedIn.
More from Modular Advantage
How Stack Modular Is Using AI to De-Risk Mid- to High-Rise Modular Construction
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept in modular construction—it is already reshaping how complex buildings are evaluated, designed, and delivered.
Gearing Up for the 2026 World of Modular
The Modular Building Institute (MBI) is bringing its global World of Modular (WOM) conference and tradeshow back to Las Vegas in April, and with it comes some of the industry’s best opportunities for networking, business development, and education.
New High-Rise Modular Apartment in Abu Dhabi Points Toward the Future of Multifamily Construction
Eagle Hills International Properties chose the BROAD Holon Building for a 16-story market rate apartment building in Zayed City, a central business district of Abu Dhabi. The project highlights the potential of the Holon system of volumetric modular construction to accelerate housing delivery.
MBI Announces First Ever Industry Apprenticeship Program in Collaboration with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center
MBI recently agreed to partner with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center (MAMC) to provide bona fide USDOL-approved apprenticeship programs for the industry.
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.