Why Modular Data Centers Are Gaining Momentum

Ron Mann is Vice President of Compu Dynamics Modular.
AI is Driving the Next Frontier for Modular Construction
Modular construction has transformed several industries, including healthcare and education, delivering speed, cost, predictability, and quality through prefabrication. Now, it’s transforming one of the most demanding sectors: IT, or more importantly, data centers.
Artificial intelligence (AI), high-performance computing (HPC), and edge applications push the limits of traditional “stick-built” data centers. They take years build, often struggle with high density workloads, and aren’t optimized for deployments near end users. Modular data center (MDC) platforms are purpose-built to address these challenges, offering flexibility and scalability to adapt to evolving technologies, while opening new opportunities for the modular construction industry.
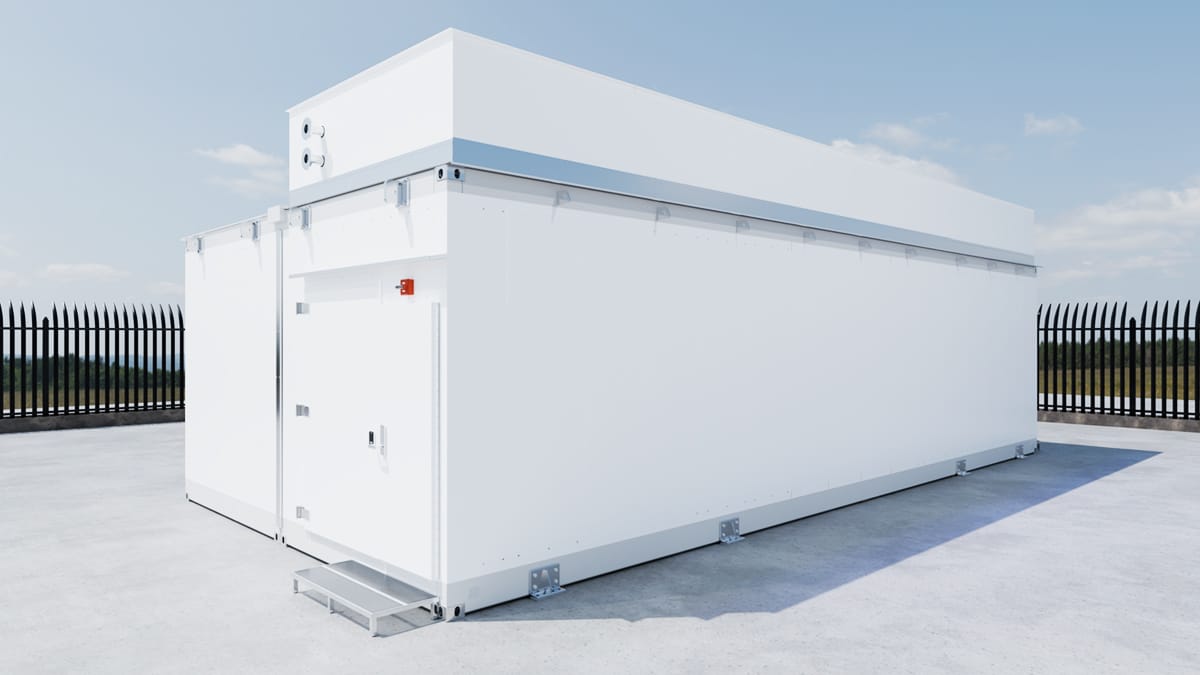

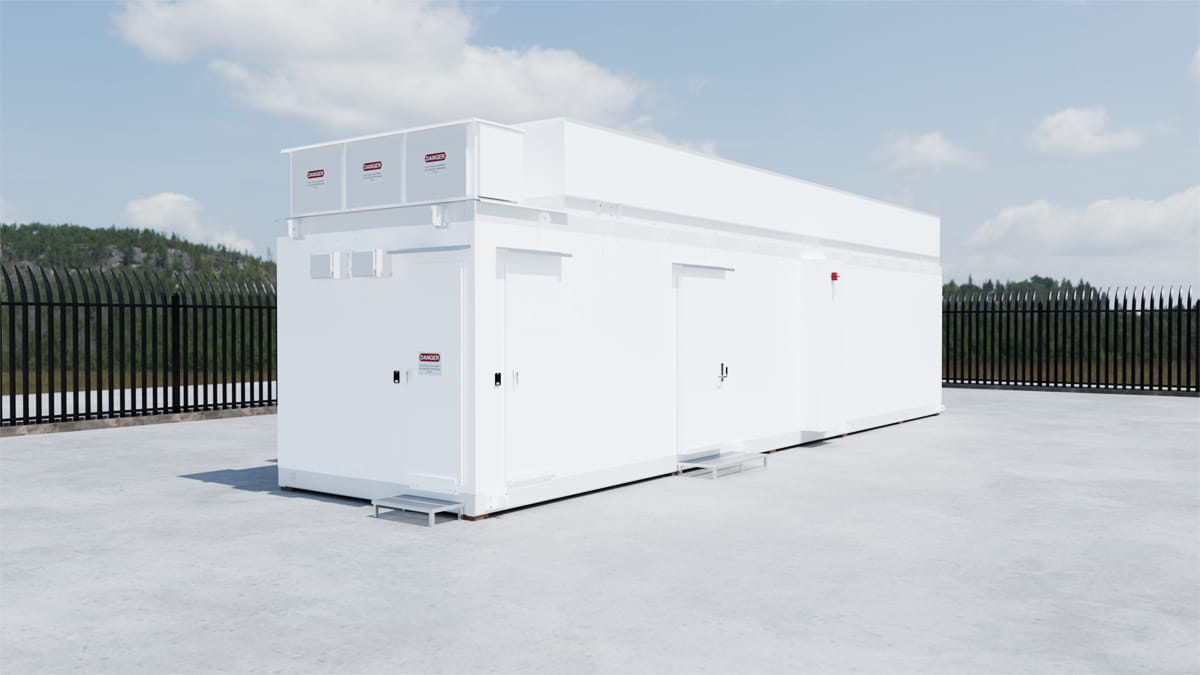
L Series Exterior view (utility, IT module and overhead cooling)
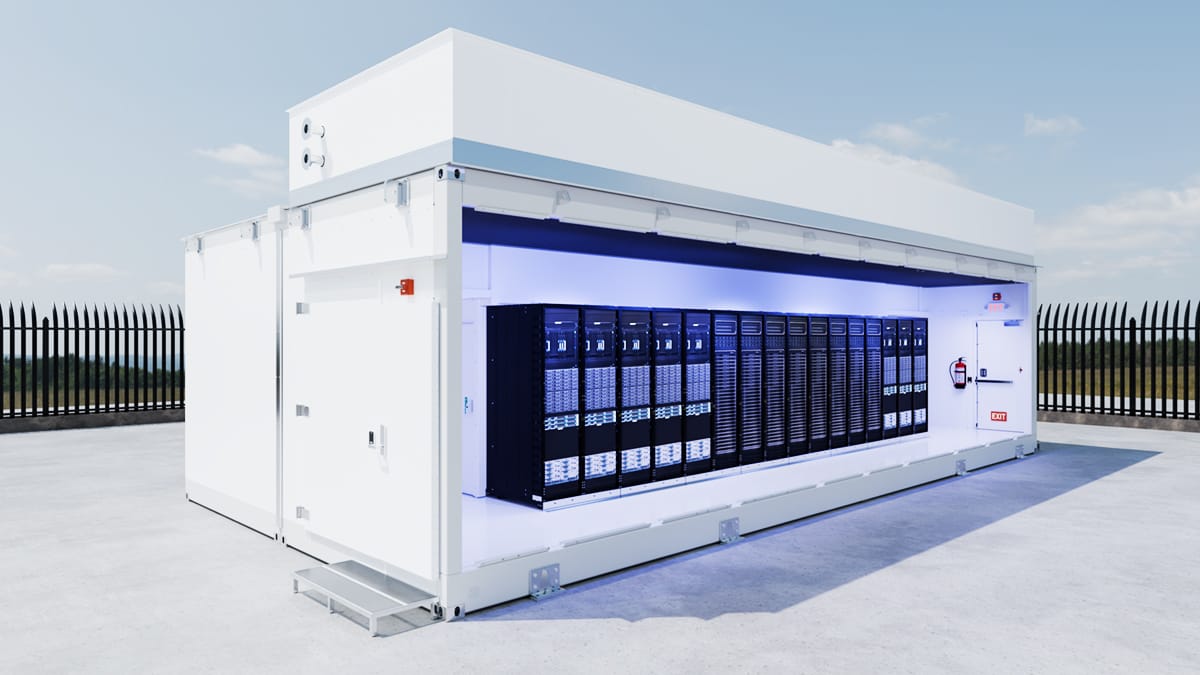

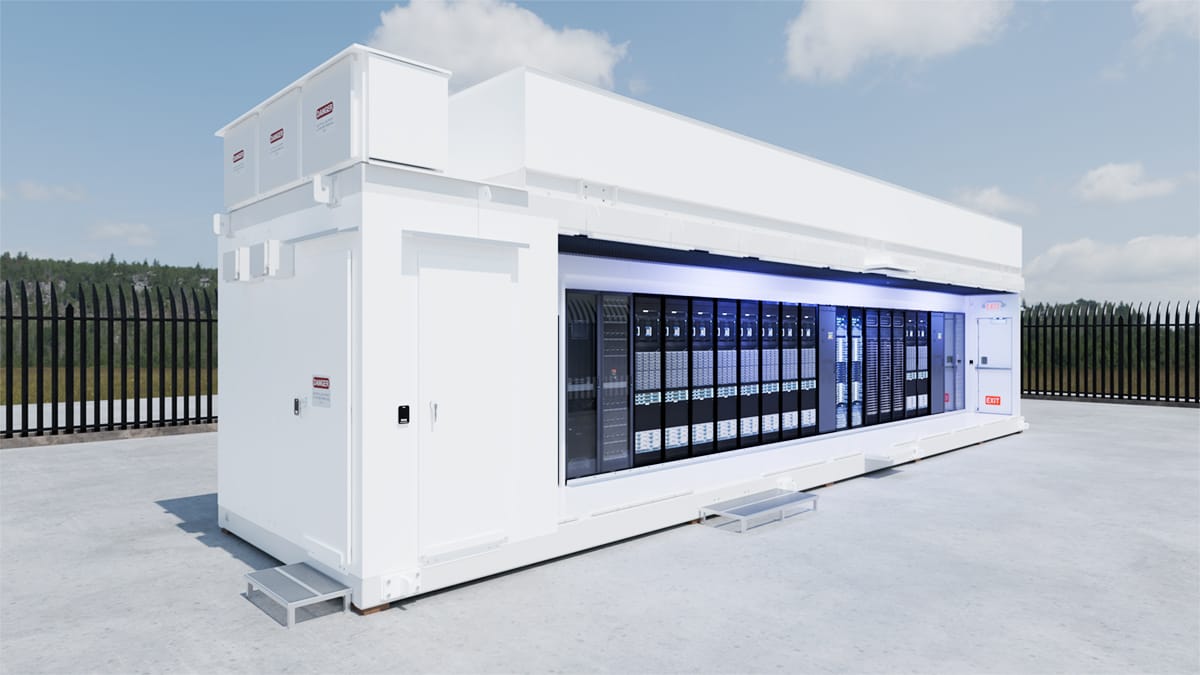
L Series cutaway view
What Makes a Data Center “Modular”?
Early MDCs have come a long way from repurposed shipping containers. While this choice offered a quick path to modularity, it was unable to support the full spectrum of IT infrastructure, especially Tier 3 or higher configurations, which require high availability and reliability.
Today’s MDCs are purpose-built in a factory setting to support specific customer applications. These units can arrive on-site, pre-tested and fully equipped with IT racks, power distribution, and cooling systems—ready for immediate deployment, and future upgrades as technology evolves. Key benefits of modular include:
- Faster schedules: Deployable in months, not years.
- Repeatable quality: Built in controlled, process driven factories, reducing onsite materials waste and workplace accidents.
- Scalable capacity: Units can be expanded, added, or reconfigured as demand grows.
- Optimized design: Modules can be tailored for customer specific applications and use cases.
Market Drivers
The rise of AI is accelerating demand for modular data centers across industries on a global scale. Factors that come into play include:
- Rising density – AI servers can draw 50–250+ kW per rack, exceeding legacy cooling capabilities.
- New cooling needs – Liquid and hybrid systems are essential for heat management.
- Latency demands – Real-time applications require compute closer to users.
- Time-to-market – Organizations can’t wait years for new facilities.
- Infrastructure agility – IT evolves rapidly, and infrastructure must keep pace.
In short, workloads are changing faster than traditional construction timelines can support.

I series exterior view (all in one module with overhead cooling system)

I series cutaway view
Two Platform Types Emerging
Compu Dynamics Modular (CDM) has developed two purpose-built platforms specifically tailored for AI workloads:
- Training/learning platforms are designed for ultra-dense compute clusters used in AI model training or HPC. These multi-megawatt systems often require liquid cooling and advanced power distribution.
- Inference platforms are smaller, self-contained units that can be deployed at the edge offering low latency for real-time decision-making, such as processing video feeds or running applications locally.
This shift reflects a broader trend: modular data centers are evolving from one-size-fits-all into specialized, application-specific solutions.
Use Cases for Modular Data Centers
The versatility of modular platforms is driving adoption in diverse settings. Take inference for example. As AI becomes more integrated into everyday operations, so does the need for compact, high-performance data centers that process information in real time. Inference modules analyze data—like video feeds or sensor inputs—on-site, enabling fast decisions without relying on distant cloud servers.
Here are examples of AI driven use cases where modular data centers can positively impact key industries:
- Autonomous vehicle R&D – Dense training clusters near testing grounds accelerate AI model development.
- Healthcare systems – Edge modules process imaging data (MRI, CT) locally, reducing latency and reliance on distant cloud centers.
- Media and entertainment – Streaming services deploy inference nodes in metro areas to bring content closer to consumers.
- Research and academia – Universities add modular pods to expand HPC capabilities without overhauling entire campuses.
These instances highlight how modular data centers extend the reach of modular construction into high-tech domains.
Key Design Considerations
For modular data center construction, several challenges stand out:
- Thermal management: At densities above 100 kW per rack, liquid cooling becomes essential. Modules must integrate plumbing and heat rejection systems efficiently and economically.
- Power distribution: High-density modules require specialized power distribution approaches and failover strategies.
- Site logistics: Site design and readiness, transport, assembly, and commissioning must be proactively planned to take full advantage of modular construction.
- Codes and standards: Electrical, mechanical, and safety codes vary by location. The UL2755 IT standard helps streamline compliance by reducing certain site-specific requirements used in traditional construction.
- Future growth: Designs must allow for expansion and technology refresh cycles without compromising capacity or uptime.
These issues are familiar to modular builders in other industries—tight tolerances, factory integration, and site coordination—but they take on added complexity in mission-critical environments.
Takeaways for the Modular Industry
Modular data centers are a natural extension of what modular construction already does well: deliver high-performance infrastructure quickly, reliably, and at scale. For firms exploring this market, here are three key insights:
- Speed, not cost, is a key driver. Just as modular schools or hospitals meet urgent needs, modular data centers address fast-moving demands in AI and digital infrastructure.
- Specialization matters. Platforms are evolving into distinct categories—dense training clusters and nimble inference nodes. Understanding these use cases will be key for construction partners.
- Integration is critical. Data centers rely on complex utility hookups (power, fiber, cooling, water). Successful projects hinge on seamless factory-to-site coordination.
Looking Ahead
As AI adoption accelerates and sustainability becomes non-negotiable, modular data centers will only grow in importance. For the broader modular construction industry, they represent both a challenge and an opportunity: a chance to apply prefabrication expertise to one of the most technically demanding infrastructure types working in tandem with IT hardware innovation.
The message is clear: modular construction isn’t just building schools, offices, or housing. It is increasingly building the digital backbone of tomorrow’s economy.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.