Building Green, Living Clean
How Modular Construction Paves the Way for Zero-Waste and Eco-Efficiency

Ali Salman is the Director of Sales and Marketing for Northgate Industries
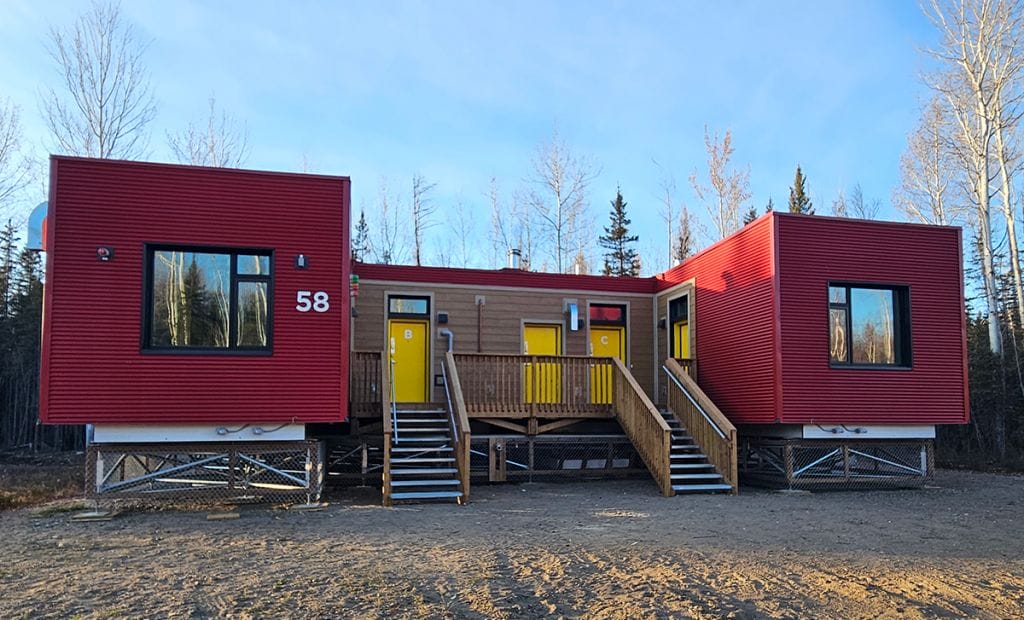
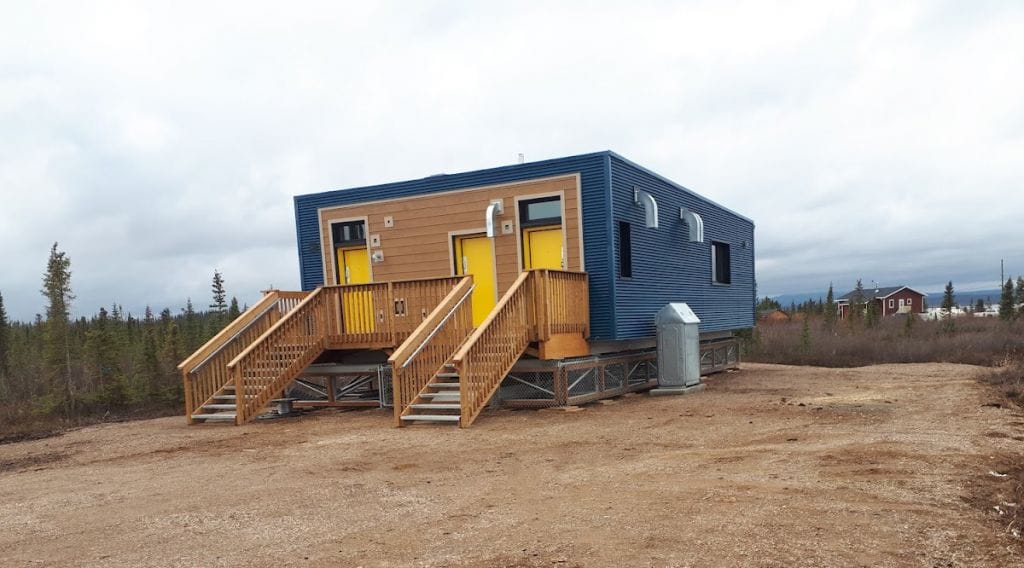
This Northern project consisted of 54 modular units making up duplexes and fourplexes with a combination of studio suites and one-bedroom suites. These units were 665 sq ft and 446 sq ft. Triodetic foundations with chain link skirting were used because of permafrost. These units were placed in 13 First Nations communities in the Northwest Territories. They were built to withstand the harshest climates, with temperatures reach down to -65 Fahrenheit, often for weeks at a time.
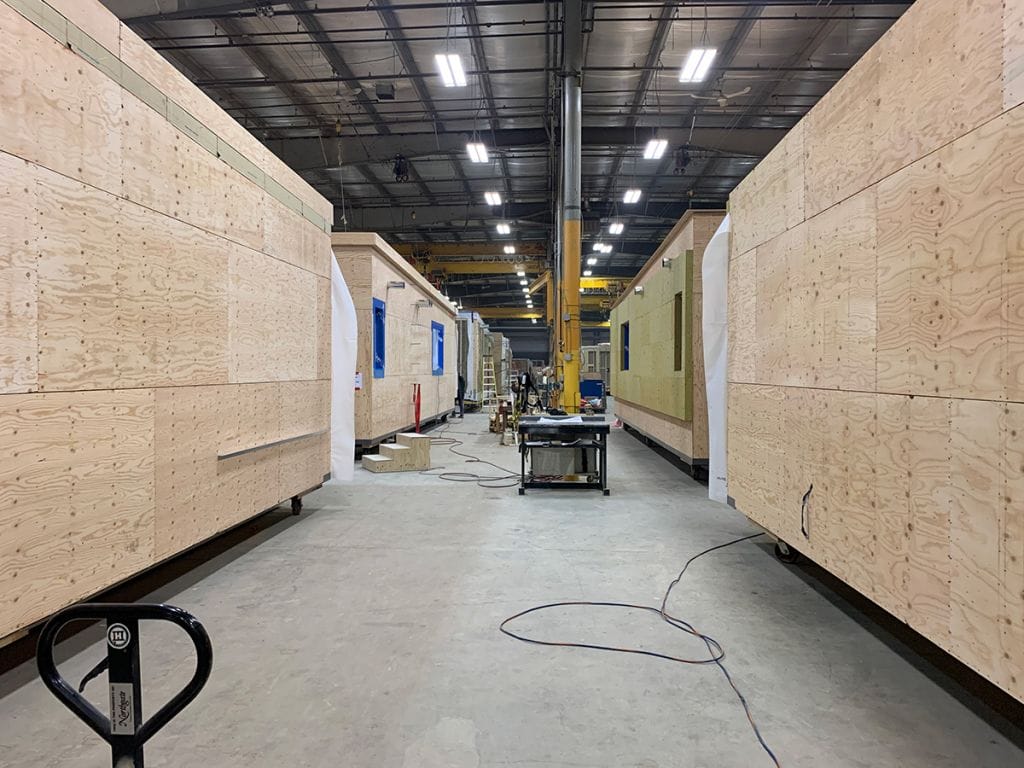
Modular construction, an innovative building method where structures are prefabricated off-site and then assembled on-site, is making significant strides in sustainable building practices. The method is increasingly recognized for its potential in achieving zero waste and superior environmental efficiency compared to traditional on-site construction. This article delves into the mechanisms through which modular construction achieves these environmental milestones, backed by statistics and research references.
Zero Waste through Precision and Recycling
Modular construction significantly reduces waste generation due to its precision and the controlled environment in which the modules are constructed. According to a report by Waste & Resources Action Program (WRAP), modular construction can reduce waste materials like timber, cardboard, plastics, and concrete by up to 90% compared to traditional construction methods. The precision of factory settings minimizes off-cuts and excess usage of materials. Additionally, any waste generated can be more efficiently sorted and recycled in a factory setting, unlike on a construction site where waste segregation and recycling can be more challenging.
Reduced Material Usage
The manufacturing process for modular buildings allows for more accurate material estimates, reducing over-ordering and excess use. This careful management of resources contributes to a reduction in the environmental impact associated with material extraction and processing. The Modular Building Institute reported that this process results in a material savings of up to 20%.
Lower Energy Consumption
Modular construction sites typically have a smaller carbon footprint. The bulk of construction activity takes place in a factory, which usually has better energy management systems than a traditional construction site. A study from the Journal of Building Engineering indicated that modular construction could lead to an average reduction in energy consumption of about 67% during the building phase. Moreover, transporting fully constructed modules to a site often requires fewer trips compared to the transportation of raw materials for on-site building, leading to reduced emissions from transportation.
Enhanced Building Efficiency
Modular buildings are often more energy-efficient than traditional buildings. The controlled environment of a factory allows for better insulation and airtightness, leading to reduced energy consumption in heating and cooling. Furthermore, research suggests that modular buildings can be up to 15% more energy-efficient than conventional buildings.
Sustainability in Material Choices
Modular construction provides an opportunity to use sustainable and recycled materials. The controlled environment of a factory allows for more experimentation and utilization of eco-friendly materials that might not be feasible in traditional construction settings.
Reduced Site Disturbance
Since most of the construction is done off-site, modular construction significantly reduces the environmental impact on the construction site. This approach leads to less soil erosion, less damage to the local ecosystem, and a reduction in the site’s carbon footprint.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its advantages, modular construction faces challenges such as transportation logistics, the need for standardization in design for more effective recycling, and perception issues in the market. However, with technological advancements and increasing awareness of environmental issues, modular construction is poised to play a crucial role in sustainable building practices.
In conclusion, modular construction presents a promising path towards zero waste and enhanced environmental efficiency in the building industry. By leveraging precision manufacturing, reduced material usage, and improved energy efficiency, this method aligns with the growing global emphasis on sustainability and environmental responsibility. As the industry evolves, modular construction is likely to become a standard bearer for eco-friendly building practices.
More from Modular Advantage
How Stack Modular Is Using AI to De-Risk Mid- to High-Rise Modular Construction
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept in modular construction—it is already reshaping how complex buildings are evaluated, designed, and delivered.
Gearing Up for the 2026 World of Modular
The Modular Building Institute (MBI) is bringing its global World of Modular (WOM) conference and tradeshow back to Las Vegas in April, and with it comes some of the industry’s best opportunities for networking, business development, and education.
New High-Rise Modular Apartment in Abu Dhabi Points Toward the Future of Multifamily Construction
Eagle Hills International Properties chose the BROAD Holon Building for a 16-story market rate apartment building in Zayed City, a central business district of Abu Dhabi. The project highlights the potential of the Holon system of volumetric modular construction to accelerate housing delivery.
MBI Announces First Ever Industry Apprenticeship Program in Collaboration with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center
MBI recently agreed to partner with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center (MAMC) to provide bona fide USDOL-approved apprenticeship programs for the industry.
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.