Affordable Housing Reimagined

Aaron Holm is the co-founder and co-CEO at Sacramento-based Blokable.
Blokable, a Sacramento-based company, is transforming the housing market, not by addressing how buildings are constructed, but by changing housing development altogether. From site selection to financing, their manufacturing-inspired model is getting rave reviews from the renewable energy community and could permanently change how housing development occurs in this country.
Blokable Roots
Blokable was started by partners Aaron Holm and Nelson Del Rio, who both experienced housing insecurity when they were young. The pair came together to solve the problems of housing and housing development. The company brings together their collective experience with product and technology development, manufacturing, finance, and law, and sees product development and manufacturing as a way to drive down the cost of housing development.
Holm says their purpose is to “change development and the way housing is built.” They believe the real issue with housing, and affordable housing in particular, is the development model. “Construction is sort of an input into the development process, the real issue that needs to be addressed is development. If you take that perspective, it changes everything because it all serves the development process, not construction per se.”
Holm believes that driving down the cost of housing development is the “holy grail” for affordable housing. Blokable set out to prove this with their flagship development, Phoenix Rising, in Washington.
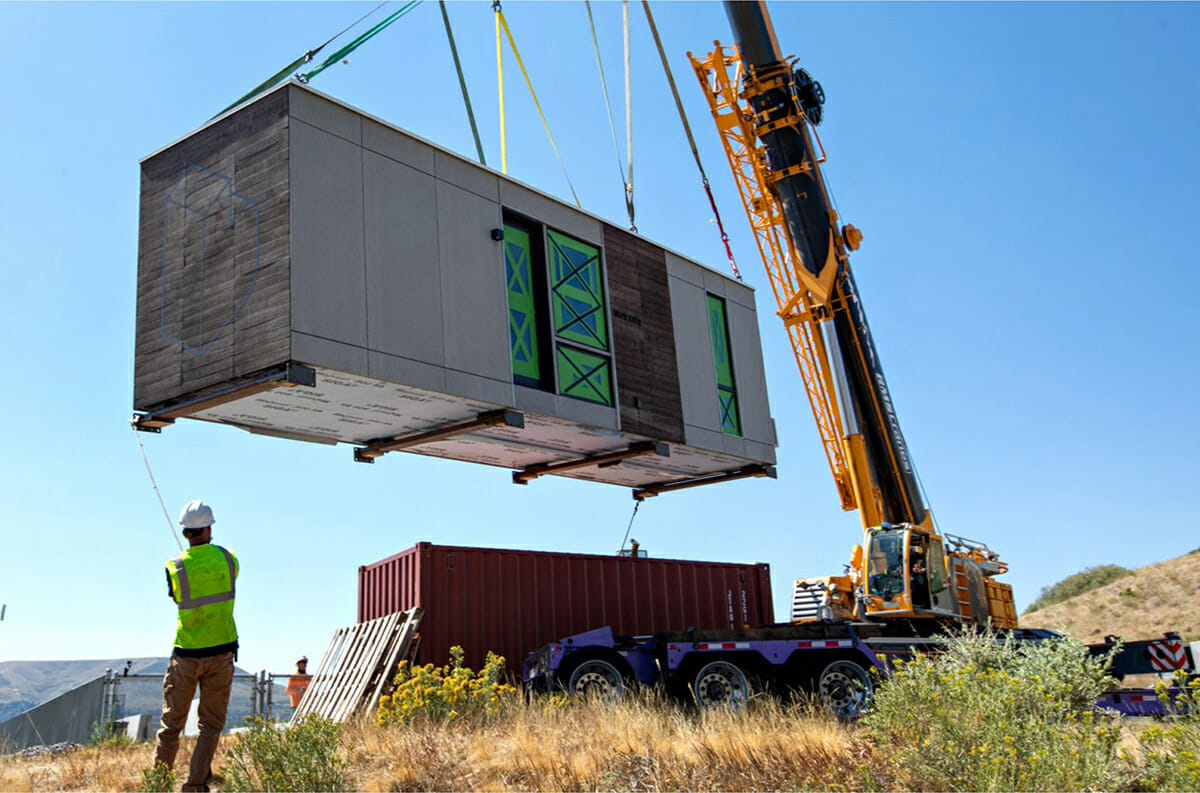

Arrival of Blokable unit at National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Golden, Co.
Phoenix Rising Project
Blokable began their transformation of the development process with a small project to test and validate their next generation structural and mechanical systems. They found a site that would allow them to build twelve connected multi-family buildings for a not-for-profit behavioral health clinic that works with teenagers recovering from substance abuse, Valley Cities.
Holm sees the lack of innovation in affordable housing as a symptom caused by the way projects are funded and go to market. Large projects don’t have the funds to pay companies to do R & D on new technologies or construction methods. And the RFP process ensures that modular construction is very rarely an option. So Holm and Del Rio had to be inventive when it came to securing financing for the project. It took a direct appropriation of funds in the state’s capital budget to ensure that the monies would go to the Valley Cities project.
Partnership with NREL
The National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL) and Wells Fargo teamed up to create a program called the Innovation Incubator (IN2). The goal of the incubator is to advance clean tech companies to market by providing up to $250,000 in technical and research support. The year Blokable got involved, the focus was on energy efficiency and multi-family development.
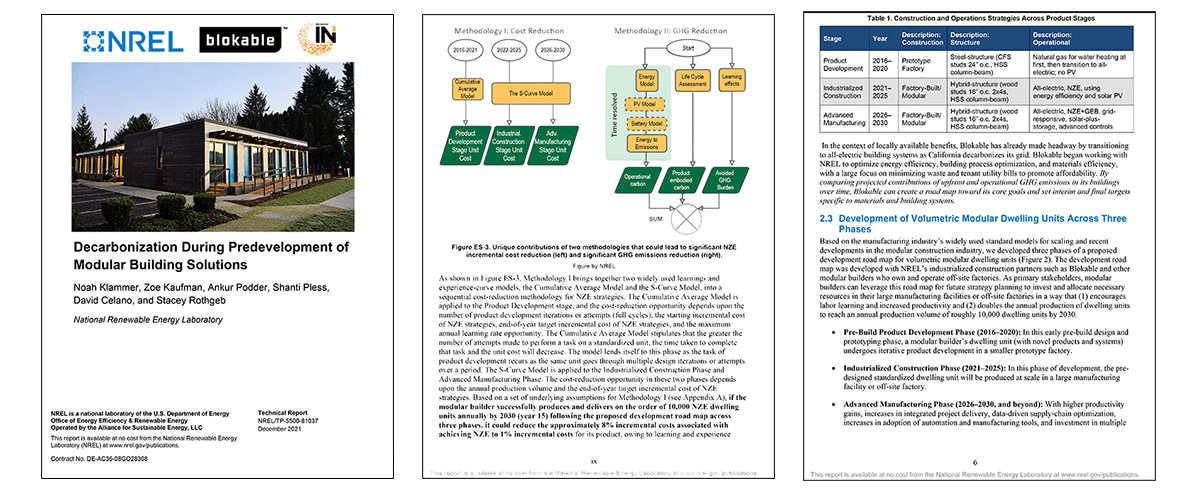
At the completion of the project and their research, Blokable and NREL worked together to author a report entitled, “Decarbonization During Predevelopment of Modular Building Solutions.” It’s considered groundbreaking in terms of what it points to in regards to how the industry can move towards net zero, all electric, and decarbonized multi-family development.
Outcomes of the Study
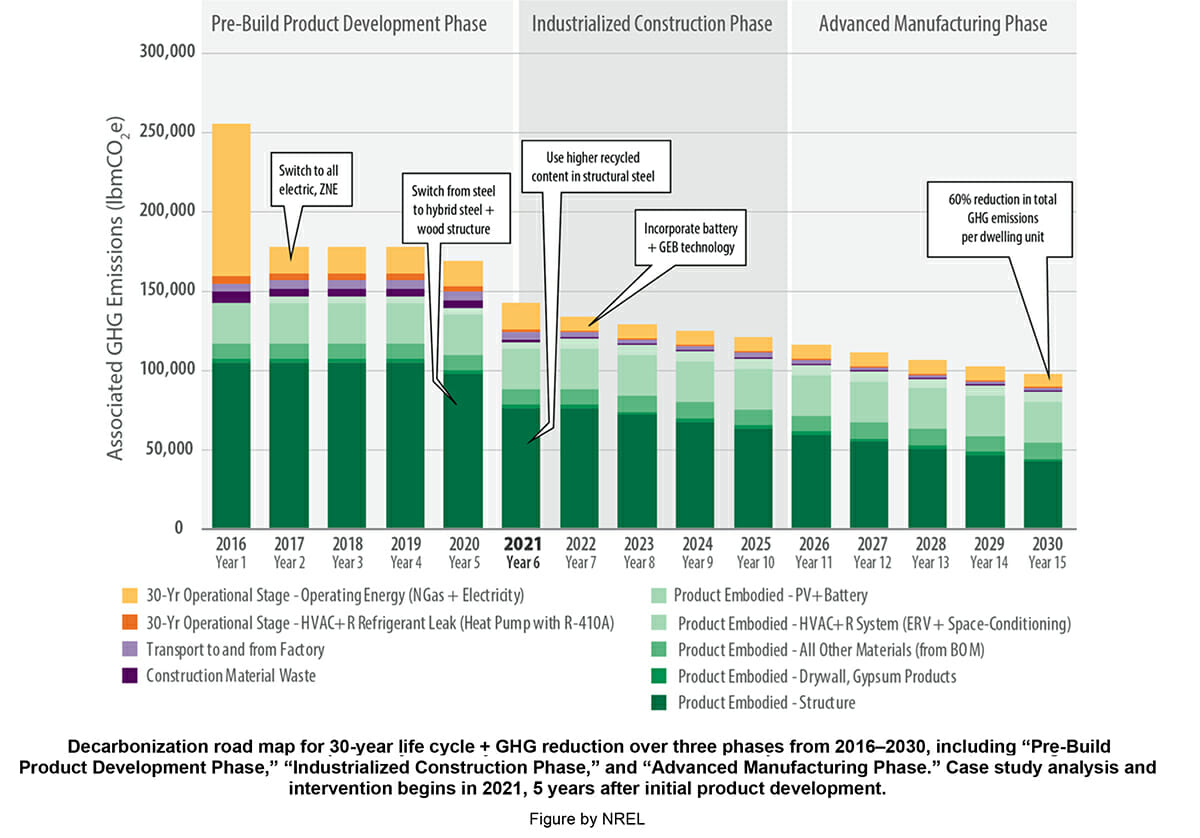
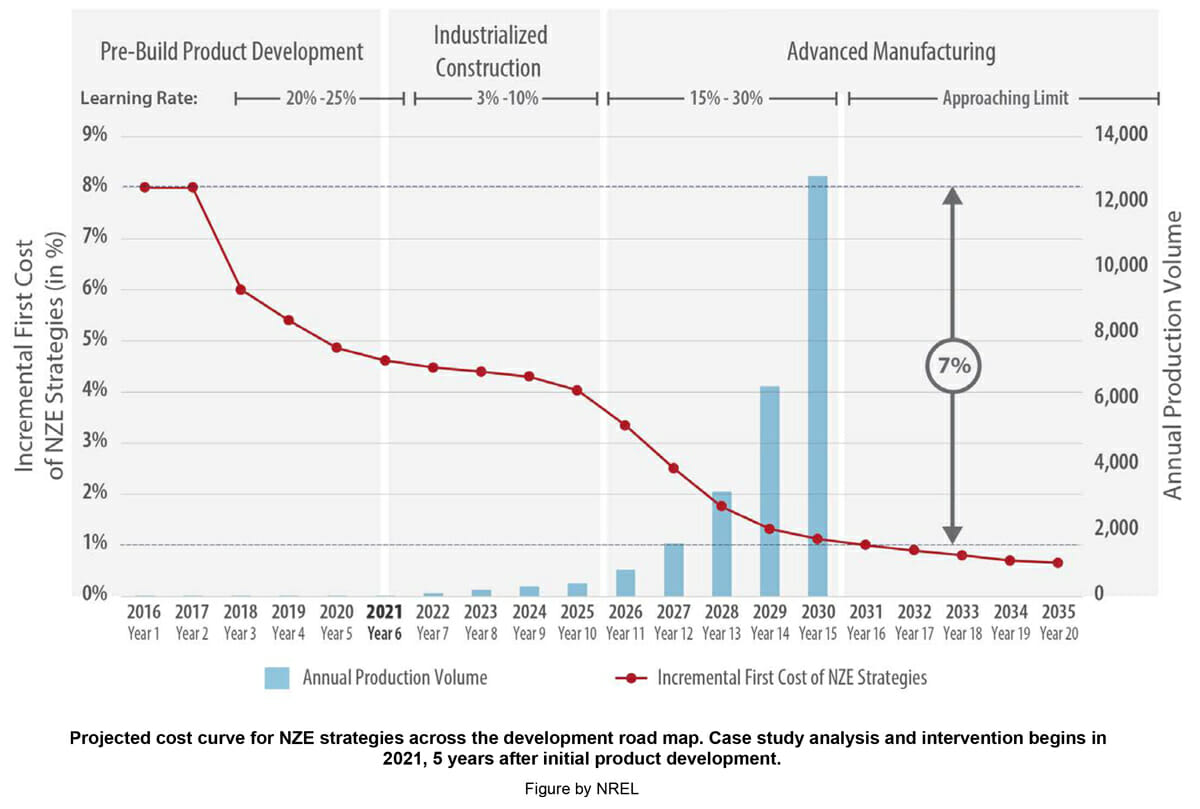
The biggest outcome of the research is the finding that when pairing construction and manufacturing, reducing energy use and decarbonizing construction doesn’t have to cost more. For the Phoenix Rising project, NREL projected the future costs of energy and the carbon impact of the dwelling units using life cycle assessment strategies. Blokable was able to achieve a projected 60% carbon reduction with essentially zero incremental cost by 2030.
The report also highlighted the fact that once a development builds to net zero energy, the next focus should be on reducing embodied carbon and adding grid-enabled technology to keep the environmental impact moving forward.
Holm believes that to continue to get these kinds of results, the industry must pivot to a manufacturing process, not a construction process.
Future of Affordable Housing Development
Based on their results, Blokable sees the future of affordable housing development as using manufacturing processes to drive costs down, then using those savings to create more compelling real estate investments.
The problem is, they didn’t get there overnight. In fact, Blokable's approach is informed by a model that Blokable's other Co-CEO Nelson del Rio successfully pioneered in commercial development in Los Angeles 30 years ago.
“The key was to spend years and a lot of money on the engineering of a building system that can be manufactured using advanced manufacturing assembly technologies, but at the same time can create really flexible floor plans and buildings that meet the market from a housing and real estate perspective,” says Holm. “The next challenge is carving out the financing and the time for early-stage prototyping, so that you know your performance before you start to scale.”
The current development model often creates incentives to provide cheap housing in order to meet the required ROI on affordable housing projects. This leaves those who can least afford it with living spaces that require a lot of energy and aren’t very healthy. By designing high quality housing units that don’t require much energy and are healthy for tenants, this new model can save developers money, requiring less subsidies and making financing easier to find. When the market provides the incentive, there will be more opportunities for modular construction like Blokable provides.
The next step for Blokable is beginning development in California, a state with some of the strictest structural and energy codes in the country. They’ve invested time and money since the Phoenix Rising project to improve the engineering of their manufacturable building system to meet California code. They are set to provide high quality housing for less cost than conventional construction methods. Their goal is to be able to provide affordable housing that leads to home ownership and equity for the residents. This builds communities and can change whole neighborhoods. In fact, they’ve seen that transformation in Washington near their first development. The corner has transformed from a crime-ridden, rough area, to one that’s lit at night, safer, and that provides the best housing for miles around.
Report: Decarbonization During Predevelopment of Modular Building Solutions
To date, net zero energy (NZE) has served as a tangible preliminary target for high-performance building in both voluntary certification programs and, now, building energy codes. Industrialized construction is one approach to efficiently achieve affordable housing that implements NZE strategies. These dwelling units are often all-electric and outfitted with rooftop solar arrays, and they produce at least as much energy through on-site renewable resources as they consume each year, enhancing energy affordability.
However, the full potential of affordable, NZE housing has not yet been tapped, due in part to incremental costs of NZE strategies surpassing traditional budgets for affordable housing projects. Additionally, as new construction becomes more energy efficient, the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the construction industry play a proportionately larger role in environmental impact and must be considered when evaluating methods of construction.
There has been limited investigation into the trade-offs between site-built and industrialized construction buildings from the perspective of reducing the incremental cost of NZE strategies and reducing GHG emissions resulting from upfront and operational emissions that are “embodied” in the building’s life.
This report details actionable pathways for the industry to leverage advanced building construction, reduce NZE incremental costs, and achieve significant GHG emissions reduction by 2030. Download the complete report at nrel.gov.
About the Author: Dawn Killough is a freelance construction writer with over 25 years of experience working with construction companies, subcontractors and general contractors. Her published work can be found at dkilloughwriter.com.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.