Modular Multi-family Construction: A Field Study of Energy Code Compliance and Performance through Offsite Prefabrication

Kevin Grosskopf is a professor at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln
Prefabrication in a factory setting may improve the performance of modular buildings compared to traditional site-built buildings. To validate this premise, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) funded a 3-year study from 2020-2023 comparing the energy performance of more than 50 modular and site-built multifamily buildings under construction in Los Angeles, San Francisco, Philadelphia and Seattle. In addition to energy performance, DOE was also interested in the potential cost savings of modular construction as well as other market opportunities and challenges.
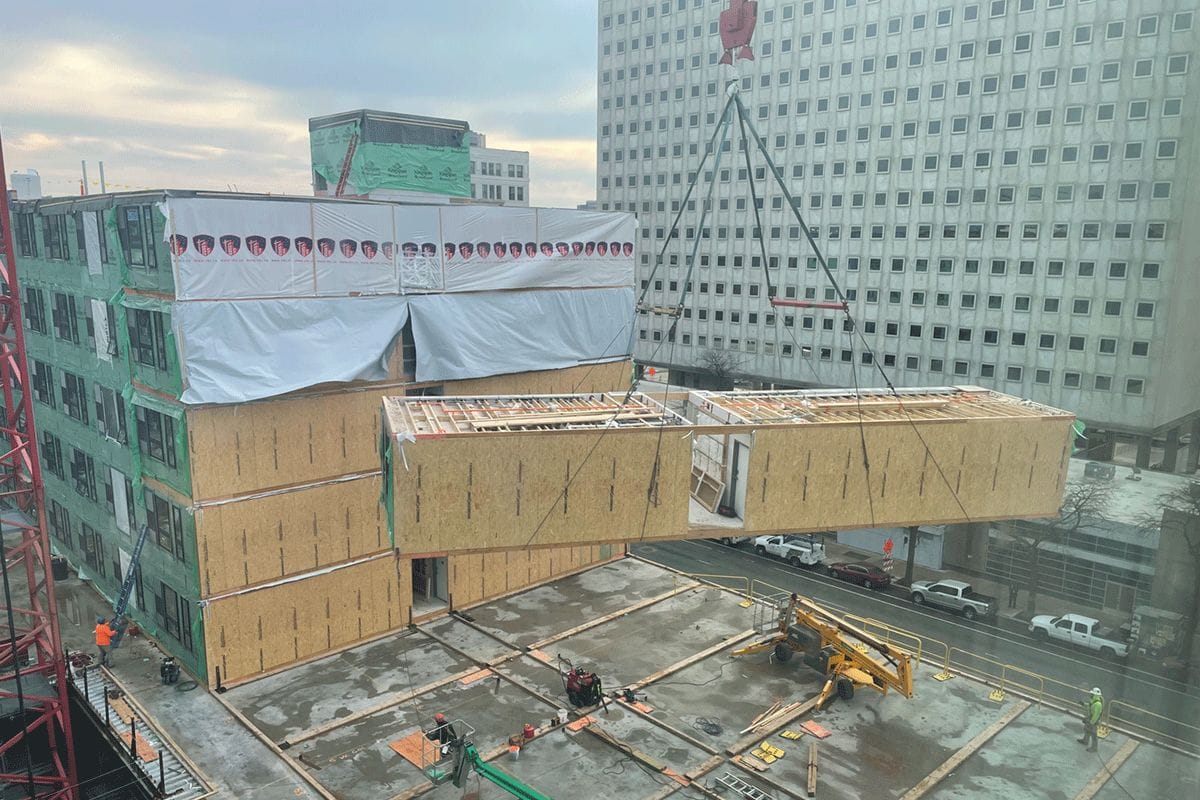

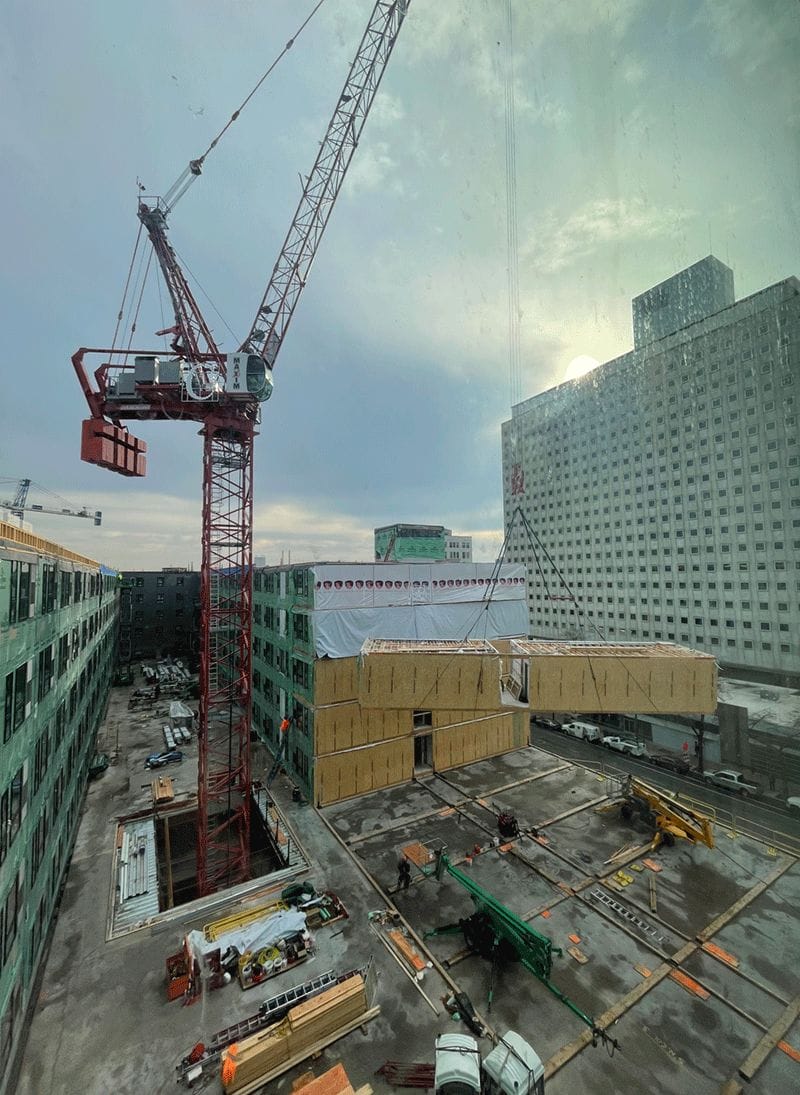
Crane set at a modular jobsite (VBC), Philadelphia PA, 2022. 260,000 sq. ft. mixed-use project consisting of 5-stories and 410 residential modular units over 2-stories of site-built commercial podium.
Part I - Energy Performance
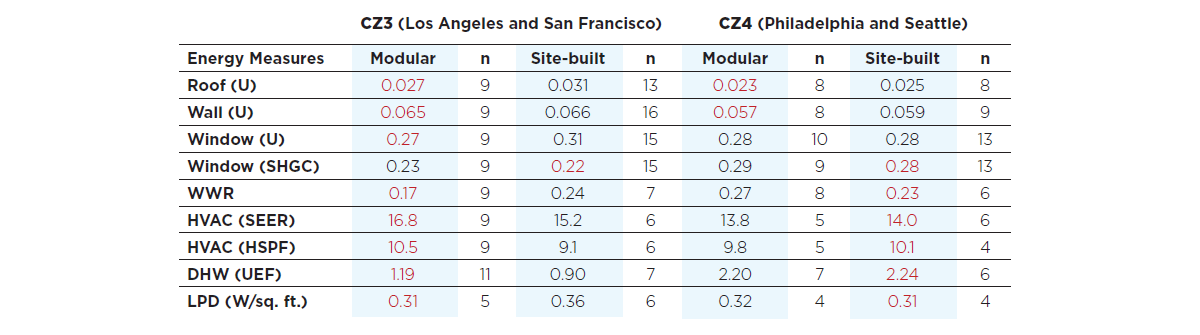
Multifamily buildings selected for this study averaged 6 stories, 140,390 sq. ft. square-feet and 144 units. Data was collected on several energy-related material and equipment systems. Data collection for each project began with a plan review followed by two field inspections. For modular projects, the first inspection was conducted at the factory and a second inspection was conducted at the construction site. Findings indicate that the performance of key energy-related materials and equipment in modular multifamily construction was somewhat better than those found in site-built, particularly in climate zones 3 (Los Angeles and San Francisco).
The DOE study also looked at the post-occupancy energy performance of another 20 modular multifamily buildings completed between 2013-2022 in these same areas. While there appeared to be little difference between the annual energy use in modular multifamily buildings (36.0 kBtu/sq. ft./yr) compared to more than 120 site-built buildings (35.8 kBtu/sq. ft./yr), ENERGY STAR™ scores for modular (86) were higher on average compared to site-built (81).
Given that most of the modular buildings in this study were affordable housing, apartment units were smaller on average (560 sq. ft.) compared to site-built units (830 sq. ft.). As a result, occupant density in modular multifamily buildings was 30-50% higher. When normalized for this, the energy performance of modular multifamily construction is likely (much) better than site-built. Although few differences were observed between the types of materials and equipment used in either modular or site-built multifamily construction, installation quality appeared to be significantly better in modular.
Part II - Market Opportunities & Challenges
During factory and construction site inspections, interviews were conducted with project stakeholders to identify key market implementation opportunities and challenges. Findings suggest that the most significant advantage of modular construction is schedule savings. Offsite prefabrication can proceed simultaneously with onsite construction, reducing time, project overhead and the impact of weather. Overall, modular buildings in this study were completed 25-30% faster on average when compared to site-built buildings. Despite added transportation costs, modular construction ($243/sq. ft.) was also found to be cost-competitive with site-built construction ($251/sq. ft.), particularly when considering shortened construction schedules and speed to market.
Yet, persistent barriers to modular market growth remain, including a building industry that is unwilling to change from traditional site-built methods, consideration of modular too late in the design process, lack of modular industry standards, and the risks associated with modular builders as a very large suppliers or subcontractors in the design-bid-build delivery process.
To address these issues, some manufacturers have undertaken a greater role in the design-manufacture-construct process. Specifically, manufacturers have begun to offer ‘turn-key’ building solutions by providing design, manufacturing and construction services in-house. By doing so, a commitment to modular is made at the beginning of the project, saving time and money. The inefficient, even adversarial relationship between designers, manufacturers, and site contractors is replaced with a single, fixed-price contract between developer and manufacturer before production begins. Profits are tied to overall project performance, not to the performance of individual players in the traditional design-bid-build process.
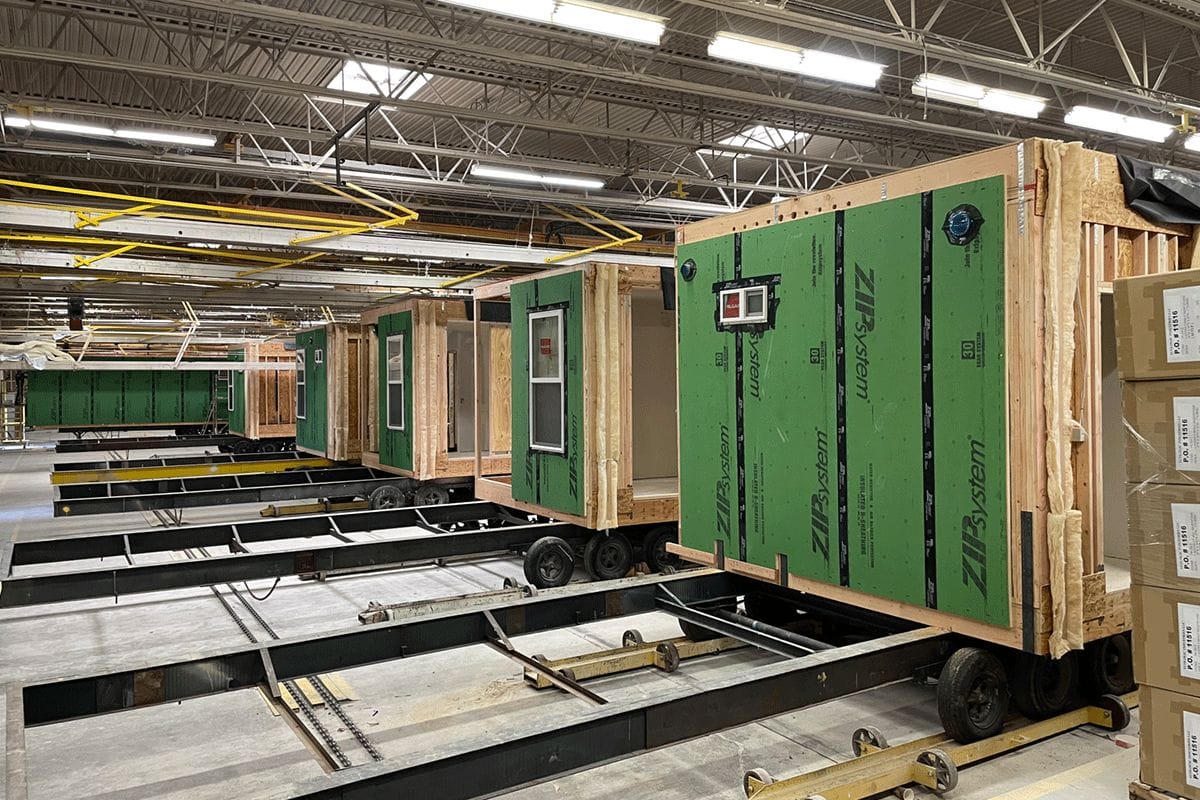


Production line at a modular factory (Nashua Builders), Nampa ID, 2023.
Conclusion
With greater control over the project design, as well as the number and timing of projects undertaken, modular manufacturers in the design-manufacture-construct process can better achieve product standardization within their factories and sustain production between project cycles. In doing so, factories can be operated more efficiently with less worker turnover.
Download the Complete Report
Download a complete copy of Kevin Grosskopf's 2023 report "Modular Multi-family Construction: A Field Study of Energy Code Compliance and Performance through Offsite Prefabrication"
More from Modular Advantage
Oregon’s Prevailing Wage Proposal: A Wake-Up Call for Modular Construction
In early February, 2024, the Massachusetts Board of Building Regulations and Standards (BBRS) released its proposed 10th Edition building codes. This draft included several amendments targeting modular construction that would have created an extremely difficult environment for the entire modular industry and could have eliminated the industry entirely in the state.
Behind the Design of Bethany Senior Terraces, NYC’s First Modular Passive House Senior Housing Project
As more developers seek to meet new regulations for energy efficiency, the team at Murray Engineering has set a new record. With the Bethany Senior Terraces project, Murray Engineering has helped to develop NYC’s first modular structure that fully encompasses passive house principles — introducing a new era of energy efficiency in the energy-conscious city that never sleeps.
How LAMOD is Using Modular to Address Inefficiency, Sustainability, and the Future of Construction
As developers, designers, and contractors seek to understand the evolving needs of the modular industry, no one is as well-versed in the benefits of going modular as Mārcis Kreičmanis. As the co-founder and CBDO of LAMOD in Riga, Latvia, Mārcis has made it his ultimate goal to address the inefficiencies of traditional construction.
From Furniture Builder to ‘Activist Architect’: Stuart Emmons’ Unique Journey
Stuart Emmons was fascinated by buildings at a young age. He remembers building sand cities with his brother during trips to the Jersey shore. His father gave him his first drawing table at the age of ten. Today, he is an experienced architect who received his FAIA in June 2025. The road he took is unique, to say the least.
Forge Craft Architecture + Design: Codes, Contracts, and Intellectual Property
Founding Principal and Director of Modular Practice for Forge Craft Architecture + Design, Rommel Sulit, discusses the implications of codes, contracts, and intellectual property on
modular construction.
Eisa Lee, the “Bilingual” Architect
Now as the founder of XL
Architecture and Modular Design in Ontario, Canada, she applies not just her education as a traditional architect but an entire holistic view on modular design. It’s this expansive view that guides her work on being a true partner that bridges the gap between architects and modular factories as they collaborate on the design process.
Tamarack Grove Engineering: Designing for the Modular Sector
The role of a structural engineer is crucial to the success of a modular project, from initial analysis to construction administration. Tamarack Grove offers structural engineering services — project analysis, plan creation, design creation, and construction administration — for commercial, manufacturing, facilities, public services, and modular. Modular is only one market sector the company serves but it is an increasingly popular one.
Engineer Masters the Art of Listening to His Customers
Since founding Modular Structural Consultants, LLC. in 2014, Yurianto has established a steady following of modular and container-based construction clients, primarily manufacturers. His services often include providing engineering calculations, reviewing drawings, and engineering certification
Inside College Road: Engineering the Modules of One of the World’s Tallest Modular Buildings
College Road is a groundbreaking modular residential development in East Croydon, South London by offsite developer and contractor, Tide, its modular company Vision Volumetric (VV), and engineered by MJH Structural Engineers.
Design for Flow: The Overlooked Power of DfMA in Modular Construction
Unlocking higher throughput, lower costs, and fewer redesigns by aligning Lean production flow with design for manufacturing and assembly.











