Aster Place by ROC Modular
The 2024 Best of Show for Relocatable Structures
Aster Place, a supportive housing building in Richmond, British Columbia, Canada, won the Best of Show Award and Honorable Mention for relocatable structures in the social and supportive housing category of the 2024 Awards of Distinction ceremony, held on the fnal evening of the 2024 World of Modular conference. The project was constructed by Tasu Construction Ltd., a general contractor from Squamish, British Columbia, and ROC Modular, a modular manufacturer in Bow Island, Alberta, and was completed in 2022.
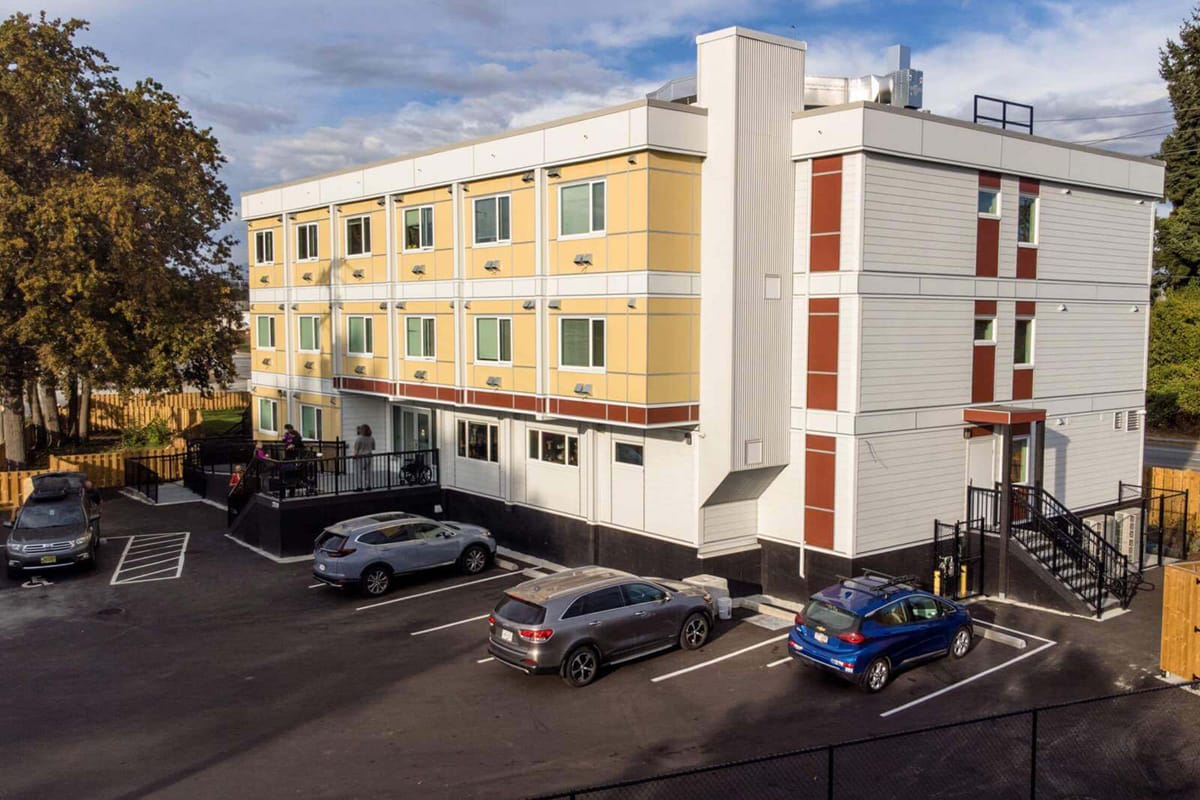

The 40-unit, 21,726 square foot temporary housing structure is part of an extensive investment by British Columbia to provide affordable housing and services for residents who are elderly, disabled, in financial need, and indigenous populations. The program, called Building BC, represents an investment of $1.2 billion over 10 years to deliver an additional 2,500 new homes in the province. Many of those new homes are benefitting from the multiple advantages modular construction provides.
The agency is focusing on underutilized sites to provide temporary housing. Aster Place is set on an existing parking lot with a Triodetic foundation.
Rhys Kane, Director of Business Development for ROC Modular, likens the foundation to a raft. “It’s a scaffold-type structure of metal and it sits as a raft slab across the top of the ground. It has these pivot points that you can adjust, and it effectively moves with the ground. It was invented and developed in northern Canada to sit above the permafrost. We’ve used it on northern projects and recognized that it was a good option for a relocatable foundation.”
The specialized foundation is a good investment because it reduces construction time and can be moved along with the building, saving the cost of another foundation.
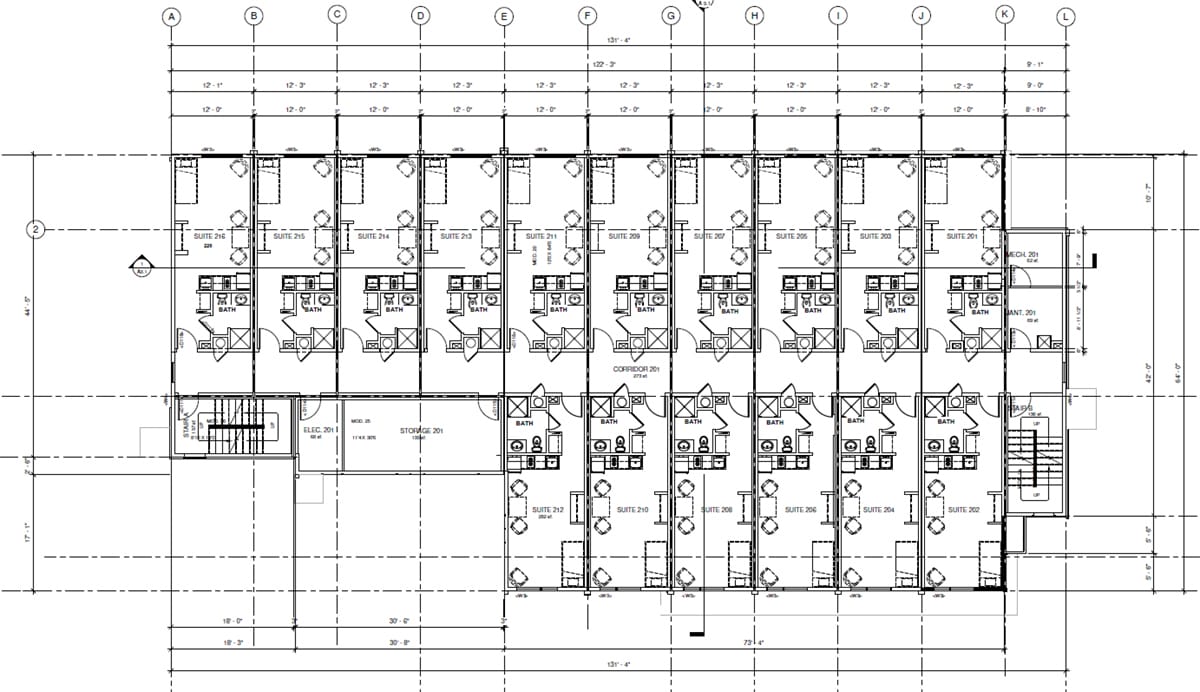
The building is three stories, with the main floor housing support services and common areas for residents, including meeting rooms,
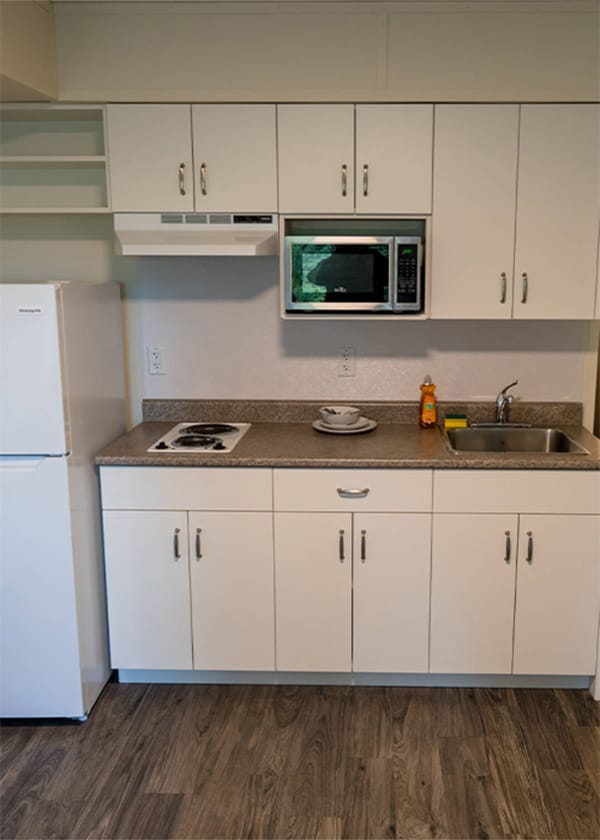
an office, a TV room, laundry facilities, storage, medical rooms, and a shared commercial-grade kitchen. Services provided include daily meals, life-skills training, employment assistance, counselling, physical and mental health resources, and access to addiction treatment and recovery services. Each unit provides a private bathroom and kitchenette.
Units come out of the factory completely finished, including mechanical systems, interior finishes, exterior finishes, kitchens, bathrooms, and even furniture, beds, and mattresses. Four of the 40 units are accessible. The project required 39 modules and took 345 days to complete.
The modules are built to meet all local building codes and permitting requirements. Aster Place meets Step Code three of the BC Energy Code, and includes features like triple pane windows, additional wall insulation, high performance mechanical systems, and LED lighting. Living units are designed to keep energy costs low for residents. The structure is set to remain on site for five to ten years while the local government explores additional housing opportunities.
Kane sees the development as a perfect showcase for how modular can help communities respond to the affordable housing crisis. “It’s very repeatable in terms of the design. There’s a template, a kit of parts to do these buildings. The modular approach is a great way to fast track. And it shows what commitment to a program can do to deliver these buildings at such speed. It takes the city of Richmond and BC Housing to say, ‘We’ve identified this site. We’re going to fast track this project, and we’re going to call it temporary. That means it avoids all the entitlements and all of the things that come with a permanent structure in terms of building permit process and timelines, which can take one to two years. And the modular company can basically repeat the modules at the factory. It provides a retained asset for the city and BC Housing that can be moved in the future.”
So far, the province has deployed over 600 housing units in similar fashion. Most are in 30-to-50-unit, three-story configurations, similar to Aster Place. The smaller-sized buildings reduce the amount of community pushback that might come with larger developments containing more units. Everything is fast-tracked through the review and permit process to speed deployment.
The project wasn’t without its struggles, of course. Since the site was in an urban environment, getting the modules to the site, setting up cranes, finding staging areas, and setting them was a challenge. The speed of design is another hurdle the team had to collaborate on to solve.
“You are delivering the project at such a fast pace, putting together the design and engineering at the same time, getting client input, and trying to meet code requirements is a challenge. We wanted to be manufacturing within six months, so there was lots of early engagement and decision making early in the process.” ROC and Tasu worked closely with suppliers, subcontractors, and the design team to ensure that the project met its budget requirements while providing energy efficiency within the short design timeframe. ROC also served as a consultant to help the team adapt modular construction techniques to the needs of the project.
ROC Modular has built over 5,000 modules and has extensive experience in creating affordable housing. They focus their services in western Canada and the north and central United States and have a 60,000 square foot manufacturing facility in southern Alberta. They specialize in social and affordable housing, hospitality, multi-family, education, and industrial modular construction. ROC gives back to the communities it serves, with a relentless focus on “creating spaces for people to thrive.”
The Aster Place development is operated by Community Builders Group, which provides culturally appropriate living assistance to those in need.


ROC Modular CEO Joe Kiss (left) and Rhys Kane (right) accept an Award of Distinction from MBI past president Chuck Walen at the 2024 World of Modular.
About the Author: Dawn Killough is a freelance construction writer with over 25 years of experience working with construction companies, subcontractors and general contractors. Her published work can be found at dkilloughwriter.com.
More from Modular Advantage
Oregon’s Prevailing Wage Proposal: A Wake-Up Call for Modular Construction
In early February, 2024, the Massachusetts Board of Building Regulations and Standards (BBRS) released its proposed 10th Edition building codes. This draft included several amendments targeting modular construction that would have created an extremely difficult environment for the entire modular industry and could have eliminated the industry entirely in the state.
Behind the Design of Bethany Senior Terraces, NYC’s First Modular Passive House Senior Housing Project
As more developers seek to meet new regulations for energy efficiency, the team at Murray Engineering has set a new record. With the Bethany Senior Terraces project, Murray Engineering has helped to develop NYC’s first modular structure that fully encompasses passive house principles — introducing a new era of energy efficiency in the energy-conscious city that never sleeps.
How LAMOD is Using Modular to Address Inefficiency, Sustainability, and the Future of Construction
As developers, designers, and contractors seek to understand the evolving needs of the modular industry, no one is as well-versed in the benefits of going modular as Mārcis Kreičmanis. As the co-founder and CBDO of LAMOD in Riga, Latvia, Mārcis has made it his ultimate goal to address the inefficiencies of traditional construction.
From Furniture Builder to ‘Activist Architect’: Stuart Emmons’ Unique Journey
Stuart Emmons was fascinated by buildings at a young age. He remembers building sand cities with his brother during trips to the Jersey shore. His father gave him his first drawing table at the age of ten. Today, he is an experienced architect who received his FAIA in June 2025. The road he took is unique, to say the least.
Forge Craft Architecture + Design: Codes, Contracts, and Intellectual Property
Founding Principal and Director of Modular Practice for Forge Craft Architecture + Design, Rommel Sulit, discusses the implications of codes, contracts, and intellectual property on
modular construction.
Eisa Lee, the “Bilingual” Architect
Now as the founder of XL
Architecture and Modular Design in Ontario, Canada, she applies not just her education as a traditional architect but an entire holistic view on modular design. It’s this expansive view that guides her work on being a true partner that bridges the gap between architects and modular factories as they collaborate on the design process.
Tamarack Grove Engineering: Designing for the Modular Sector
The role of a structural engineer is crucial to the success of a modular project, from initial analysis to construction administration. Tamarack Grove offers structural engineering services — project analysis, plan creation, design creation, and construction administration — for commercial, manufacturing, facilities, public services, and modular. Modular is only one market sector the company serves but it is an increasingly popular one.
Engineer Masters the Art of Listening to His Customers
Since founding Modular Structural Consultants, LLC. in 2014, Yurianto has established a steady following of modular and container-based construction clients, primarily manufacturers. His services often include providing engineering calculations, reviewing drawings, and engineering certification
Inside College Road: Engineering the Modules of One of the World’s Tallest Modular Buildings
College Road is a groundbreaking modular residential development in East Croydon, South London by offsite developer and contractor, Tide, its modular company Vision Volumetric (VV), and engineered by MJH Structural Engineers.
Design for Flow: The Overlooked Power of DfMA in Modular Construction
Unlocking higher throughput, lower costs, and fewer redesigns by aligning Lean production flow with design for manufacturing and assembly.










