Demand Booms for Modular Cleanrooms: G-CON Delivers

José Negrón is a process architect at G-CON, a manufacturer of prefabricated modular cleanrooms.
José Negrón is a process architect at G-CON, a manufacturer of prefabricated modular cleanrooms, which the company calls PODS. His role involves a combination of engineering and architecture. At the beginning of a project, his goal is to fully understand all the steps of the client’s production process, “starting from how they get raw materials into their warehouse; how they check the quality of the materials; every step of their production line; the flow of people and materials through the process; all the way to the finished product going out the door.” With that understanding, Negrón can design a POD layout that best serves the client’s processes and equipment.
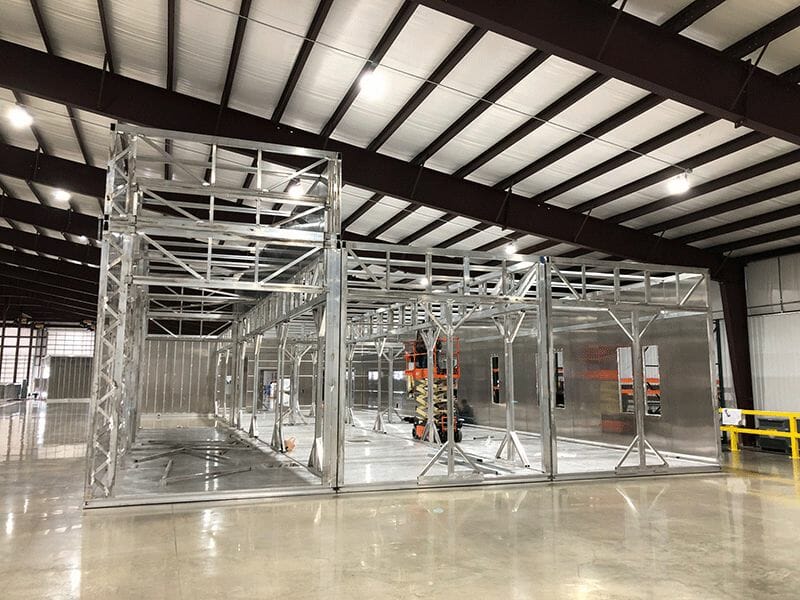

The PODs structures are made by welding aluminum members. Some extrusions are patented aluminum shapes that provide higher load bearing capacity than typical extrusions.
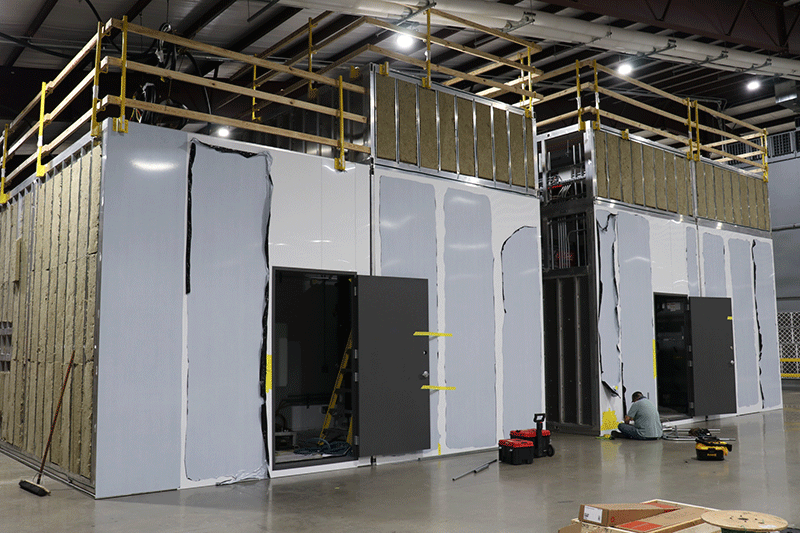

The PODs are fit-out at the factory with the necessary architectural components, in addition to the mechanical, electrical, automation and fire protection systems.
Product Design
Cleanrooms often have smaller rooms adjacent to them, called airlocks. Airlocks are used for people to gown-up, or for materials to go in or out. These actions take place in the airlocks so the proper environmental conditions can be maintained inside the cleanroom. Depending on the process, some airlocks are bi-directional, and some are uni-directional.
The superstructure of each cleanroom POD is made of aluminum, which is strong, light, and corrosion-resistant, all significant advantages over steel and wood construction. G-CON builds each POD frame in their fabrication shop. “The PODs are then combined with pre-assembled architectural and mechanical systems,” Negrón says.
“Fresh outside air is pre-conditioned with a make-up air unit to remove particulates and to get the temperature and humidity within a certain range,” Negrón explains. “Within each POD, there’s a dedicated HVAC system that receives the pre-treated air and pushes it through a number of filters. The final HEPA [High Efficiency Particulate Air] filters are in the cleanroom ceiling.”
Once the air flows into the cleanroom and reaches the floor, low wall return chases remove it from the room. “Any particulate matter that might be in the air goes down to the floor and out through the low wall returns,” Negrón adds. This airflow ensures no particulates accumulate in the corners of the cleanrooms. Coving where the walls meet the floor and ceiling also help achieve this.
Strict Requirements
In the pharmaceutical industry G-CON serves, there are different regulatory requirements for various aspects of a client’s processes. For example, air cleanliness and room classification requirements will vary depending on a client’s manufacturing processes.
In addition, many clients have very specific, rigorous cleaning protocols for every surface of the cleanroom, including the floor, walls, and ceiling. The materials for the interior surfaces must be able to withstand the cleaning chemicals used and the cleaning frequency.
In many cases, G-CON’s clients need to be able to prove to regulatory agencies that their products — such as vaccines — have been manufactured within strict environmental parameters. This means they must collect data on air temperature, relative humidity, air pressure, and other factors. “The data needs to be digitally collected, saved, and protected in such a way that nobody can tamper with it,” Negrón explains. “So, if someone from the regulatory agency asks for the data regarding a specific batch of vaccines manufactured at a certain time on a certain date, all that data is available.”
Modular Manufacturing Advantages
Building in a controlled, indoor environment means that it’s much more feasible to keep the product clean during construction. “Before shipping, we have a list of tests we perform on each POD in the factory. After they’re tested, the PODs are prepared and shrink-wrapped for shipping and delivery,” Negrón says. Once the cleanroom PODs are installed at the client’s facility, G-CON cleans them again. “For commissioning, we test the POD systems once more.” The client then does the final sanitization prior to operation.
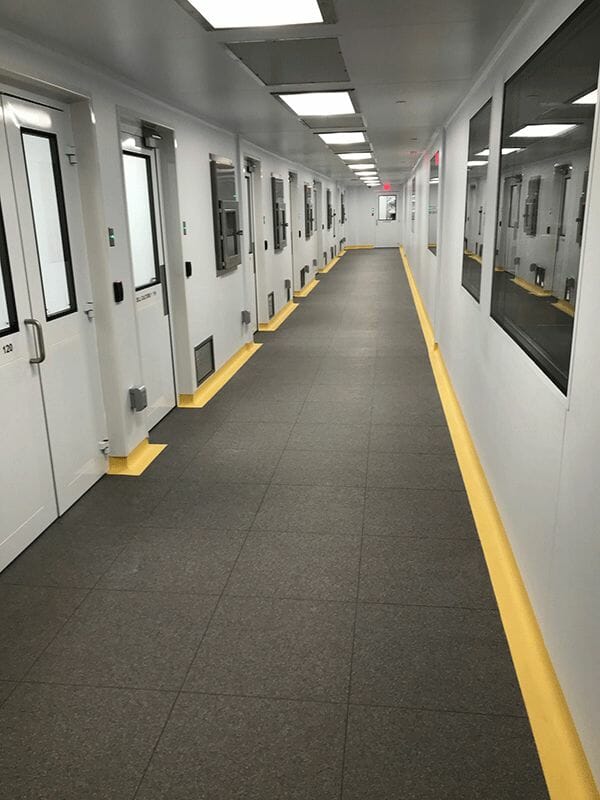

SubPODs are joined together with clean corridors that lead to airlocks, pass-through boxes and other material transfer elements.
Negrón says that more and more clients are turning to prefabricated modular cleanrooms “because of the high quality, cost certainty, predictable schedules, and the ability to deliver projects much faster than traditional construction.”
Another advantage of POD cleanrooms is that they can be used temporarily and then re-located. Clients can use the cleanrooms for as long as they need them and then re-deploy them for another use or sell them. With traditional stick-built cleanrooms, the building expenses are sunk costs because the cleanrooms can’t be moved or re-sold as independent units if they’re no longer needed. Also, a small manufacturer can begin operating with one cleanroom POD and add more as the company grows and requires additional capacity — because each POD is completely self-contained.
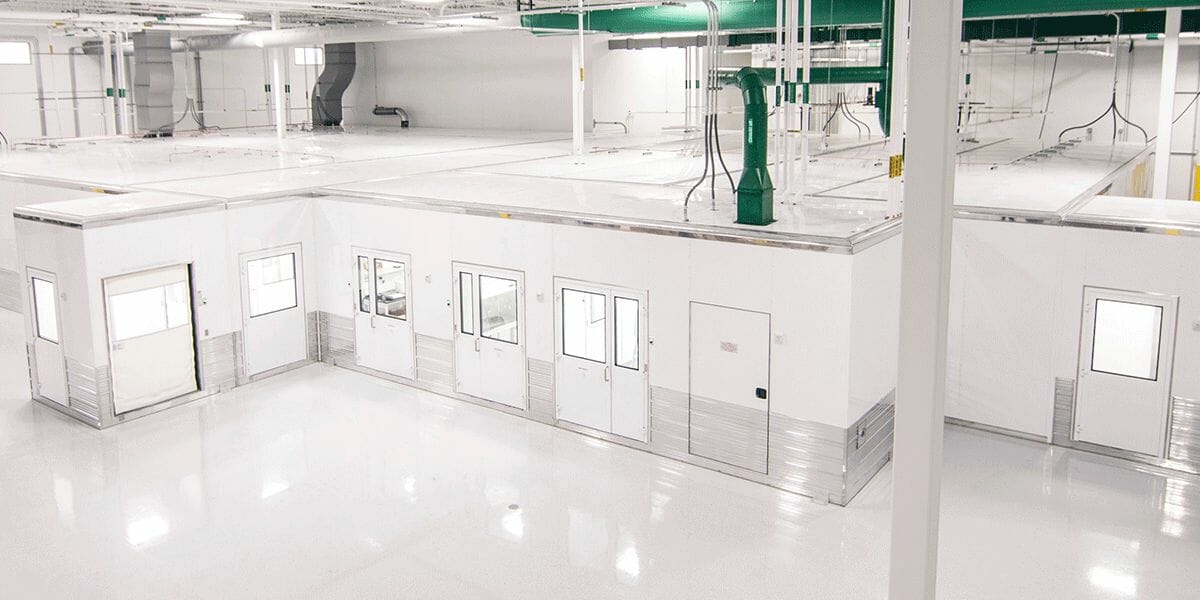

Depending on the client’s process, subPODs can be joined together to form a POD cluster. Projects vary from 1 to 14 plus subPODs. Interconnecting the PODs allows clients to have great layout flexibility.
Greater Demand and Increasing Standardization
The demand for cleanrooms has been very high over the past couple of years. “When COVID hit, some clients put projects on hold. But we were also inundated with new requests for cleanrooms, to support the global COVID response, including vaccine manufacturing,” Negrón says.
This increased demand has resulted in rapid growth for G-CON, including greater manufacturing footprint, capacity, and head count. At the same time, G-CON is moving towards more standardization of its POD systems to further reduce the time and cost for delivering cleanroom facilities. The company recently released a catalog of standardized POD designs. These standard models can address the needs of cell and gene therapy companies, or can handle fill-finish. (Fill-finish is the final step of filling, labeling, and packaging vials of medications before they’re distributed.) The idea is that the standardized PODs will provide enough variety and flexibility for clients to mix and match, while also providing the speed advantages of standardization. “Standard PODs can be ready for delivery in three months, whereas if a client requires custom POD designs, it might take six months to a year to deliver the PODs, depending on the project size,” Negrón says.
World of Modular Presentation
The main focus of Negrón’s World of Modular presentation is to show how G-CON delivers projects faster than regular construction methods, helping companies take drugs and therapies to market faster, saving patients’ lives. Cleanrooms must adhere to strict standards imposed by regulatory bodies such as the FDA, and Negrón will talk about how the manufacturing process for cleanrooms differs from ordinary modular prefabrication.
About the Author: Zena Ryder is a freelance writer, specializing in writing about construction and for construction companies. You can find her at Zena, Freelance Writer or on LinkedIn.
More from Modular Advantage
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.
Art²Park – A Creative Application of Modular and Conventional Construction
Art²Park is more than a park building—it’s a demonstration of what modular construction can achieve when thoughtfully integrated with traditional materials. The use of shipping containers provided not only speed and sustainability benefits but also a powerful structural core that simplified and strengthened the rest of the building.
Building Smarter: A New Standard in Modular Construction Efficiency
Rising material prices, labour shortages, expensive financing and tightening environmental rules have made conventional construction slower, costlier, and more unpredictable. To keep projects on schedule and within budget, builders are increasingly turning to smarter industrialized methods.
Resia: Breaking All the Rules
Resia Manufacturing, a division of U.S.-based Resia, is now offering prefabricated bathroom and kitchen components to industry partners. Its hybrid fabrication facility produces more precise bathroom and kitchen components (modules) faster and at lower cost than traditional construction. Here’s how Resia Manufacturing does it.
How LINQ Modular Innovates to Bring Modular To The Market in the UAE and Beyond
LINQ Modular, with an office and three manufacturing facilities in Dubai, is a modular firm based in United Arab Emirates. The company is on a mission: to break open the housing and construction markets in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) area with modular.