Modular or Offsite Construction is About the Process First, Product Second, Project Third

About the Author: Blair Davies, P.Eng. MBA, is the chief operating officer at Catalyst Offsite. An expert in modular building and facade systems that are innovative, aesthetic, sustainable, constructible, affordable and proven. With 30+ years in complex roles of leadership in design, manufacturing, strategy, sales and marketing in multiple industries, provides his clients with unique points of view on problem analysis, solution generation and implementation.
Having engaged many clients in the transition to offsite construction, something has become very clear: If owner/developers start by thinking offsite construction is simply traditional construction with a factory, they have it backwards. Let’s dig further.
Note: This discussion comes from an understanding of steel offsite construction, but many of the key tenets apply to other types of systems.
First some definitions and key roles:
Offsite construction: Major assemblies or subassemblies, the ‘product’ is produced in a factory and then shipped to a building site and assembled as a building. In Modular products are stacked to make a building or project. In other varieties, as in prefab walls, subassemblies are shipped to site for building assembly.
Volumetric Modular: The product, a module or room, is built in a factory, complete with frame, floor, walls, bathrooms, or kitchens as required. Sometimes furniture is included. The most integrated solution is one in which the space is ready to be occupied once services are connected. Modules can also be delivered in various intermediate stages (e.g., a frame of an unfinished module).
Process: The steps and roles to achieve the desired result.
Product: The module, which will be made in a factory.
Project: The building required to meet an end customer’s need. Sometimes the project is a repeatable template, e.g., a template 5 storey building on a podium, expected to be deployed several times. Or a project is a specific building for a specific site. Hint the money is doing the former.
Key metrics: The activity, to speak generally, starts with some targets of price, cost, grade of building (maybe 1-5 star like a hotel), finishes, throughput or quantity over time. Etc. These should be set at the beginning and tracked as the activity comes to fruition.
DFMa: Design for Manufacturing and Assembly. A key part of the process to deem how the product can be made in a factory. Note it is not design for construction, or design for project. The game i.e., budget, quality, on time delivery, is all set by getting the Product designed correctly for the target factory.
Parametric Modelling: Manufacturing requires a different view on design. The output of DFMa needs to be a very granular and exact product design in a form that can be managed with the supply chain. The product is best if it can be modified on the fly using parametric solutions. The system COCo uses is SolidWorks.
BIM: Building Information Modeling. Note the first word is Building. Therefore, BIM—often done in tools like Revit—applies to the Project. While BIM is used in building design, it does not suit manufacturing and supply chain management.
Factory Readiness: The culmination of work on process, product, and project is the factory readiness. It indicates that design fits manufacturing, the supply chain is established, key personnel are in place and trained, and workflow is designed and established. To put it simply, what will come in the front door and what will go out the back door to meet target cost, throughput, and quality.
The Modular Construction Process
So, what are we seeing? Developers, often in response to RFQs or their own project needs, start with the project. What kind of building do they want to build? Accustomed to traditional construction, they hire an architect and go down the path of designing the building completely, applying for permits, and preparing to make what was designed. For offsite and modular construction, this is wrong.
The correct steps, as shown here, are:
1. Project: What is needed: Very general, limited design: just layout and space planning. Initial targets are set. A multifunctional team can be involved. A trial business case is explored here. Everything of the effort will return to measure against these goals, and possibly modify the goals. Very general design—not specific project design—is the goal.
2. Module: What will be manufactured. A small team of module expert personnel, plus some support personnel create a granular, costed, exact bill of materials. The module or product is modelled, from the frame to full system. Get this right and the Project will go well.
3. Project: Now design a building or project. Take the Product or Module and apply it to a building. Discuss the mate lines, hallway dimensions, location of elevators, access, lobby, building dimensions, structural engineering, services, local codes. Almost like traditional architectural and engineering building design, but with the Module or Product as a key building block.
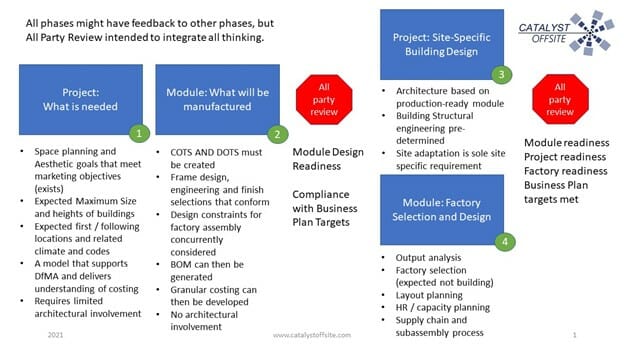
4. Factory: As design begins, factory selection can also start. Assuming an existing building will be selected for the factory, select the right one. Conceptual layout, throughput, material input, product exit, shipping access, storage, personnel… all the things it takes to run a factory.
All-party reviews: During the entire process, the teams—for which there are common personnel—constantly exchange information that might modify decisions or bring issues to light, but the formal all-party reviews are key. All-party reviews are meetings with a cross functional team of management, finance, module or product design, building or project design, the architect(s), the engineer(s), and maybe even the customer. This group comes together and provides their guidance on any diversions from the goals. Once all input is given, a priority-based decision-making process is created and followed. Then the various members of the team go back to their work with this guidance.
Learn More in this Podcast:
Best Practices—and Processes—of Modular Construction Projects w/ Catalyst Offsite
Blair Davies, P.Eng, COO of Toronto-based Catalyst Offsite, joins the podcast to discuss the processes necessary to properly plan and start a modular building project.
Blair also talks about common mistakes that first-time modular building developers make and shares best practices learned over decades in the building industry.
Is This Process Linear As Shown?
No. We are seeing developers and builders who have offsite projects, or win RFQs, before they have decided on a Product. A metaphor would be to design and build a car while driving down the highway in it. It won’t work. It is imperative not get sucked into the vortex of designing the project (step 3) before following step 1 and 2. A premature full architectural design will waste time and money, typically result in a Product that is not manufacturable, miss cost targets, and not take advantage of the state-of-the-art attributes of Process and Project available within offsite construction. A simple example is in stage 2 the team is offered a Revit model of a Project, expecting the team to come up with a Product in parametric modelling. It just does not work that way.
How Do Things Go Incorrectly?
Simple: Traditional construction starts with step 1, goes to step 3 with no product really considered. For example, when step 3 is chosen, a decision is made whether to build a wood, steel, or concrete frame, and all other components, subassemblies and assemblies are specified by the architectural team since most projects are not repeated. With offsite construction, following steps 1-4—in order—is critical for the success of the project.
Process Comes First
If you are considering entering the offsite or modular building community, learn about the offsite process then transition and establish the right team to meet your business targets. Do not start with the building you want to design and offer.
Catalyst Offsite can guide you through and assist in your success. There is more to this, including what goes on in the factory, why precision matters, how modular building effects what goes on site, and other considerations.
Learn more and contact Blair Davies directly at Catalyst Offsite.
More from Modular Advantage
Oregon’s Prevailing Wage Proposal: A Wake-Up Call for Modular Construction
In early February, 2024, the Massachusetts Board of Building Regulations and Standards (BBRS) released its proposed 10th Edition building codes. This draft included several amendments targeting modular construction that would have created an extremely difficult environment for the entire modular industry and could have eliminated the industry entirely in the state.
Behind the Design of Bethany Senior Terraces, NYC’s First Modular Passive House Senior Housing Project
As more developers seek to meet new regulations for energy efficiency, the team at Murray Engineering has set a new record. With the Bethany Senior Terraces project, Murray Engineering has helped to develop NYC’s first modular structure that fully encompasses passive house principles — introducing a new era of energy efficiency in the energy-conscious city that never sleeps.
How LAMOD is Using Modular to Address Inefficiency, Sustainability, and the Future of Construction
As developers, designers, and contractors seek to understand the evolving needs of the modular industry, no one is as well-versed in the benefits of going modular as Mārcis Kreičmanis. As the co-founder and CBDO of LAMOD in Riga, Latvia, Mārcis has made it his ultimate goal to address the inefficiencies of traditional construction.
From Furniture Builder to ‘Activist Architect’: Stuart Emmons’ Unique Journey
Stuart Emmons was fascinated by buildings at a young age. He remembers building sand cities with his brother during trips to the Jersey shore. His father gave him his first drawing table at the age of ten. Today, he is an experienced architect who received his FAIA in June 2025. The road he took is unique, to say the least.
Forge Craft Architecture + Design: Codes, Contracts, and Intellectual Property
Founding Principal and Director of Modular Practice for Forge Craft Architecture + Design, Rommel Sulit, discusses the implications of codes, contracts, and intellectual property on
modular construction.
Eisa Lee, the “Bilingual” Architect
Now as the founder of XL
Architecture and Modular Design in Ontario, Canada, she applies not just her education as a traditional architect but an entire holistic view on modular design. It’s this expansive view that guides her work on being a true partner that bridges the gap between architects and modular factories as they collaborate on the design process.
Tamarack Grove Engineering: Designing for the Modular Sector
The role of a structural engineer is crucial to the success of a modular project, from initial analysis to construction administration. Tamarack Grove offers structural engineering services — project analysis, plan creation, design creation, and construction administration — for commercial, manufacturing, facilities, public services, and modular. Modular is only one market sector the company serves but it is an increasingly popular one.
Engineer Masters the Art of Listening to His Customers
Since founding Modular Structural Consultants, LLC. in 2014, Yurianto has established a steady following of modular and container-based construction clients, primarily manufacturers. His services often include providing engineering calculations, reviewing drawings, and engineering certification
Inside College Road: Engineering the Modules of One of the World’s Tallest Modular Buildings
College Road is a groundbreaking modular residential development in East Croydon, South London by offsite developer and contractor, Tide, its modular company Vision Volumetric (VV), and engineered by MJH Structural Engineers.
Design for Flow: The Overlooked Power of DfMA in Modular Construction
Unlocking higher throughput, lower costs, and fewer redesigns by aligning Lean production flow with design for manufacturing and assembly.










