Relocatable Buildings vs. Permanent Modular Construction: What's the Difference?
Modular construction is revolutionizing the construction industry as a super-efficient and sustainable solution for building faster, stronger, and more predictably.
There are two types of modular structures- Relocatable Buildings and Permanent Modular Construction. While both construction types offer a plethora of benefits, there are distinct differences.
In this article, we'll help you understand the differences between permanent modular construction and relocatable buildings.

This hospital in New York is an MBI Awards of Distinction-winning example of permanent modular construction.
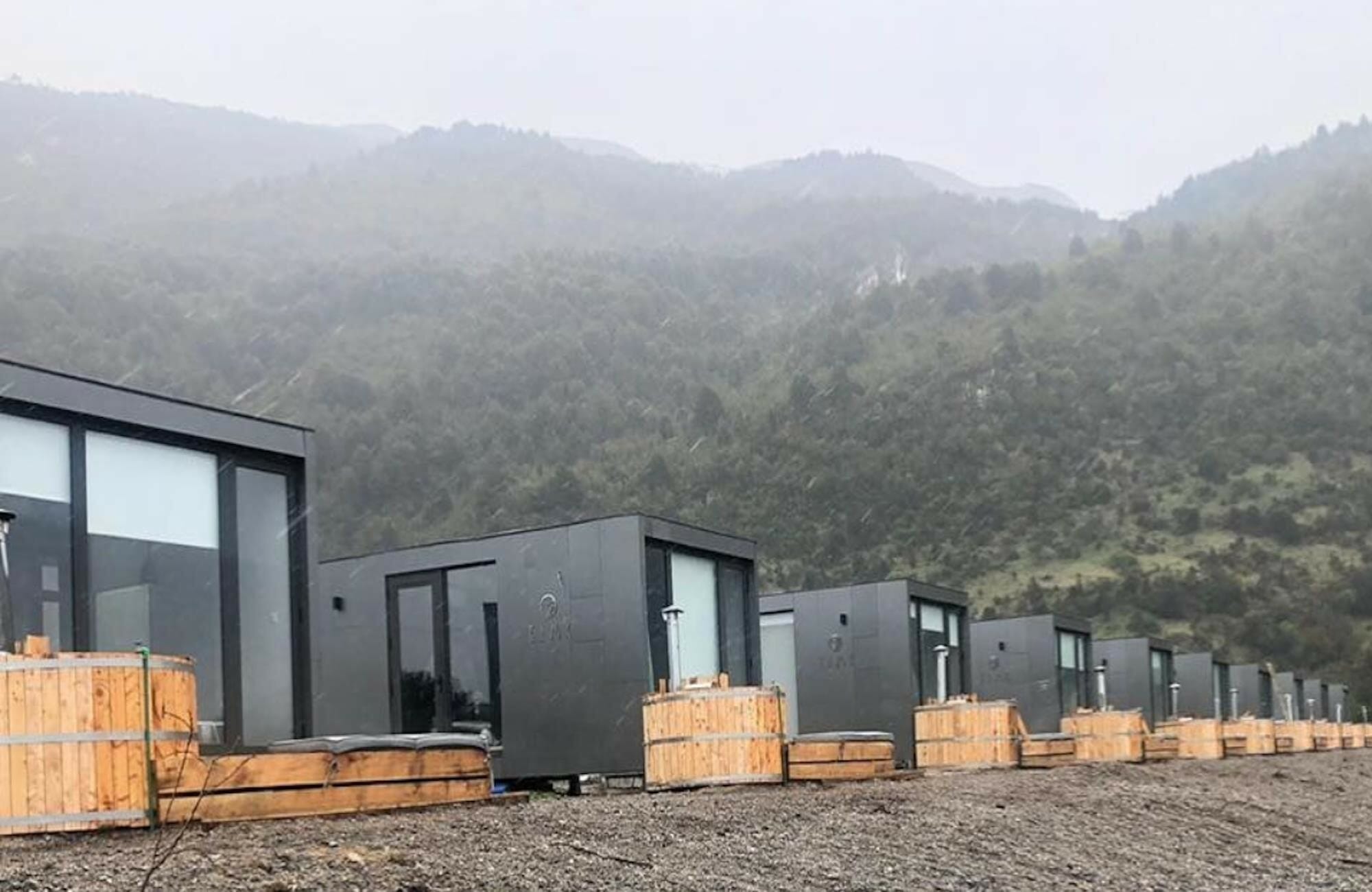

These luxury cabins are an MBI Awards of Distinction-winning example of relocatable buildings.
What is Modular Construction?
Also known as volumetric construction, modular construction uses individual sections or modules, which are assembled off-site in factories under controlled conditions, to create complete structures of all shapes and sizes.
The modules themselves use the same designs and materials as traditional construction and meet all the same building standards and codes. The modules are then transported and put together at the final construction site.
There are two main methods of modular construction:
Permanent Modular Construction (PMC)
PMC is a sustainable and innovative building technique that utilizes offsite and lean manufacturing methods to prefabricate either single or multi-story structures in modular sections. PMC can be integrated into an existing structure or can be built to stand independently. The modules can then be completed with MEP interior finishes, fixtures, and appliances. The Hawaii Film Studio, for example, used PMC to meet strict timeline and budget requirements. Other examples of permanent modular construction include healthcare facilities, hotels, schools, and restaurants.
Relocatable Buildings
Also known as portable buildings, RBs are partially or completely constructed structures that also abide by set building codes and are assembled in a controlled manufacturing facility through the modular construction process.
Relocatable buildings are made to be repurposed and transported to various building sites. They can be used for medical clinics, schools, sales centers, and construction sites, among others.
The Differences Between Relocatable and Permanent Modular
1. Duration Of Use
Permanent modular structures are fabricated and installed for long-term use. They are designed to be durable, just like conventional buildings, and can last just as long (or longer) than traditionally-constructed buildings.
Relocatable buildings, on the other hand, are installed for a shorter intended duration; a few months or a year, for instance. They are also designed durable enough to withstand several relocations and installations.
2. Types of Materials Used
Because permanent modular structures are intended for longer use, they are typically constructed with wood, steel, and/or concrete. Relocatable buildings, on the other hand, are usually made of wood to make them lightweight and easier to transport and reinstall.
3. Building Purpose
Permanent modular buildings are designed to remain in one location for an extended period of time.
Temporary modular buildings are ideal for situations that demand quick construction and future relocation and repurposing. They are mostly built to offer temporary housing such as, construction sites, or mobile showrooms, as well as for some commercial purposes.
4. Architecture
When it comes to architecture options, temporary modular structures offer less design and layout choices. They also offer fewer options for customization.
Though the architect's plans for PMC must be settled well before construction begins, permanent modular buildings offer nearly endless options. From the addition of lobbies to elevators and stairwells, these structures offer construction engineers and consumers alike countless design possibilities.
5. Construction Duration
While the duration of construction will depend on the scope of work, relocatable buildings have the potential to be on-site and ready to use within weeks.
On the other hand, permanent modular buildings may take months or more to construct and assemble on-site based on the structure's size and design. Despite the differences between the two types of modular construction, both types offer owners many benefits. The benefits include: less material waste, faster completion of projects because of indoor construction, safer construction, and a quicker return on investment. For a complete list of the Modular Building Institute's PMC and RB manufacturers, click here.
More from Modular Advantage
How Stack Modular Is Using AI to De-Risk Mid- to High-Rise Modular Construction
Artificial intelligence is no longer a future concept in modular construction—it is already reshaping how complex buildings are evaluated, designed, and delivered.
Gearing Up for the 2026 World of Modular
The Modular Building Institute (MBI) is bringing its global World of Modular (WOM) conference and tradeshow back to Las Vegas in April, and with it comes some of the industry’s best opportunities for networking, business development, and education.
New High-Rise Modular Apartment in Abu Dhabi Points Toward the Future of Multifamily Construction
Eagle Hills International Properties chose the BROAD Holon Building for a 16-story market rate apartment building in Zayed City, a central business district of Abu Dhabi. The project highlights the potential of the Holon system of volumetric modular construction to accelerate housing delivery.
MBI Announces First Ever Industry Apprenticeship Program in Collaboration with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center
MBI recently agreed to partner with Marshall Advanced Manufacturing Center (MAMC) to provide bona fide USDOL-approved apprenticeship programs for the industry.
AoRa Development Aims for New York’s First Triple Net Zero Building Using Modular Methods
More cities are providing funding for newer infrastructure projects as long as they meet sustainability requirements. This is how modular can fit the bill, thanks to its lower waste production.
Developers and Designers: Lessons Learned with Modular Design
Modular construction is attractive to many developers because sitework and module construction can occur simultaneously, shortening the schedule and reducing additional costs.
UTILE: Putting Modular Building on a Fast Track
In Quebec, UTILE is taking the lead in creating affordable modular buildings to help decrease the student housing shortage. During the process, the company discovered what it takes to make the transition to modular building a success.
Sobha Modular Teaches Developers How to Think Like Manufacturers
With its 2.7 million square foot factory in UAE, Sobha Modular is bringing both its high-end bathroom pods to high-end residences to Dubai while developing modular projects for the U.S. and Australia.
RoadMasters: Why Early Transport Planning is Make-or-Break in Modular Construction
In modular construction, transportation is often called the “missing link.” While it rarely stops a project outright, poor planning can trigger costly delays, rerouting, and budget overruns.
Navigating Risk in Commercial Real Estate and Modular Construction: Insights from a 44-Year Industry Veteran
Modular projects involve manufacturing, transportation, and on-site assembly. Developers must understand exactly what they are responsible for versus what they subcontract. Risk advisors should research the developer’s contractors, subcontractors, and design-build consultants—especially the modular manufacturer.